-

The wall text accompanying these charts in the Hunterian museum, Glasgow, reads: "In the late 19th and 20th centuries, before the advent of colour slides that could be projected, the teaching of Zoology depended heavily on the use of wall charts to illustrate lectures. They were hung on a special pulley system at the front of the lecture theatre and, because of their large size, could be clearly seen from the back of the class".
-

“On two occasions in 1977, when a patient’s left ventricle failed acutely after routine open-heart surgery and when no human donor organ was available, Barnard transplanted an animal heart heterotopically. On the first occasion, a baboon heart was transplanted, but this failed to support the circulation sufficiently, the patient dying some six hours after transplantation. In the second patient, a chimpanzee heart successfully maintained life until irreversible rejection occurred four days later, the recipient’s native heart having failed to recover during this period. Further attempts at xenotransplantation were abandoned and even now, more than 30 years later, xenotransplantation remains an elusive holy grail despite decades of research.”
Extract: Brink JG, Hassoulas J. The first human heart transplant and further advances in cardiac transplantation at Groote Schuur Hospital and the University of Cape Town. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2009; 20(1):31-5
-
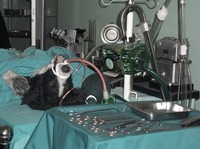
The guided tour of the museum, which commemorates the first heart transplant performed by Chris Barnard in 1967, starts with a representation of the car accident that provided the heart for the transplant, through to the animal lab where Barnard conducted experiments with over 50 dogs to perfect the technique of heart transplantation. From there one can tour a model of Denise Darvall's bedroom and Christiaan Barnard's office before seeing a recreation of the surgery in the actual operating theaters where it occurred.
-

On Feb. 2, 1903, English physicians William Bayliss and Ernest Starling, gave a lecture on the digestive system to a theatre full of medical students. Also in attendance were Lizzy Lind af Hageby and Leisa Schartau, committed feminists and anti-vivisectionists. They had travelled from Sweden to enrol at the London School of Medicine for Women, attend lectures around town, and document the practice of vivisection in British universities.
During the lecture, a brown terrier was wheeled out, strapped to a board. Starling had already performed one experiment on the dog two months earlier, shutting off its pancreas. This time, Bayliss cut open the dog’s neck and spent half an hour unsuccessfully trying to stimulate the animal’s salivary glands with electrodes. Eventually, he gave up and handed the dog over to a student (Henry Dale, another future Nobel laureate) who stabbed it through the heart, thus ending the lesson.
What followed was a court case filed by Stephen Coleridge, a prominent barrister and secretary of the National Anti-Vivisection Society against Bayliss. After four days of testimony, the judge called the women’s account “hysterical” while giving instructions to the jury. The jurors conferred for 20 minutes, then found Coleridge guilty of libel.
Anti-vivisectionists commissioned a bronze statue of the dog as a memorial, unveiled in Battersea in 1906. Its plague, which read "Men and women of England, how long shall these Things be?" led to the it being vandalised on a frequent basis. On 10 December 1907, hundreds of medical students marched through central London waving effigies of the brown dog on sticks, clashing with suffragettes, trade unionists and 300 police officers, one of a series of battles known as the ‘Brown Dog’ riots.
In March 1910, tired of the controversy, Battersea Council sent four workers accompanied by 120 police officers to remove the statue under cover of darkness, after which it was reportedly melted down by the council's blacksmith.
-

In 1999, Jaak Panksepp and Jeffrey Burgdorf successfully demonstrated that tickling young rats spurs them into letting out the same ultrasonic giggles they make during play.
-

Cyanotype on paper. Ink on perspex.
The work shows the exact positioning of the stars from J.M. Barrie’s window at 3 Adelphi Terrace, London (51°30'N 0°7'21"W), on Saturday, 19 June 1937 – the night of his death. Based on the direction of his window, I was able to locate the ‘second star to the right’ at the 45 degree angle he would have stood and viewed the night sky. Hopefully, he reached his destination, after departing the flat and traveling ‘straight on till morning’.
-

Marine biologists studying whalesharks use the pattern-recognition technique, developed in 1986, that astronomers use to analyze data from the Hubble Space Telescope. Studying the spatial relationships between a whaleshark's spots form the basis for creating a unique identifier for each shark.
-

Published in 1841, Jackson’s guide was the first of a series of guides published during this period which offered notes for the traveller on appropriate conduct in the field – from providing methods for training the eye to observe what was deemed as relevant details, to instructions on which precision instruments should be carried and how to use them to record and inscribe the results of observations made (Withers 2013: 170). As Jackson states, his guide pointed out to the “uninitiated Traveller what he [sic] should observe, and to remind the one who is well informed, of many objects which (…) might escape him” (Jackson 1841: i).
-

In 2015, Conservation International scientists in Indonesia attached satellite transmitters to the dorsal fins of whale sharks to learn more about their migratory movements and diving behavior. Dipsy, a 4.57-meter male, spent much of his 17-month deployment in Triton Bay but also visited the Aru and Kei Islands – one of our first Kaimana whale sharks to explore the Arafura Sea – before returning to Kaimana. He hit a maximum depth of 625 meters.
-

In 2015, Conservation International scientists in Indonesia attached satellite transmitters to the dorsal fins of whale sharks to learn more about their migratory movements and diving behavior. Yoda had a lengthy 26-month deployment, spending all of that time in Cendrawasih Bay. The 4.83-meter male dove to a maximum depth of 1,375 meters, reaching the bottom of the bay at one of its deepest points.
-

In 2015, Conservation International scientists in Indonesia attached satellite transmitters to the dorsal fins of whale sharks to learn more about their migratory movements and diving behavior. At just 3 meters in length (about 10 feet), Fijubeca logged an impressive 9,000 kilometers (5,592 miles) during his deployment. He visited eight of the Bird’s Head Seascape's marine protected areas (MPAs), reaffirming the placement of MPAs as related to megafauna migratory routes.
-

In 2015, Conservation International scientists in Indonesia attached satellite transmitters to the dorsal fins of whale sharks to learn more about their migratory movements and diving behavior. Sunbridge was one of our first sharks tagged in Saleh Bay, Sumbawa, where he spent his entire 14-month deployment. Though this 6.23-meter male spent a fair bit of time on the surface, he frequently visited the bay's bottom at a maximum depth of 350 meters.
-

In 2015, Conservation International scientists in Indonesia attached satellite transmitters to the dorsal fins of whale sharks to learn more about their migratory movements and diving behavior. Sebastian spent most of his 27-month deployment in Cendrawasih Bay but also recorded a visit to the Mapia atoll and ventured past Biak into PNG coastal waters. He eventually returned to Cendrawasih, where his tag's battery expired, having logged a maximum dive of 1,125 meters.
-

The Brazilian artist Lygia Clark (1920-1988) produced relational objects to be inhabited and activated by groups of people. Her net made up of elastic bands attached to each other, allows a complex structure, a complex grid, inviting a choreographed dance between strangers as they play with it by pushing and pulling these bands.
-

"Early Pacific seafarers did not have scientific instruments or conventional European-style maps to voyage to, and settle, the thousands of islands of Micronesia and Polynesia. Instead they used the movement of the sea, the direction of the wind, the position of the sun and stars, and the flight of birds. This is a navigation chart, obtained by Georg Irmer, the Governor of the Marshall Islands from Chief Nalu of Jaluit atoll in 1896. The strips of wood, bound by cane, represent the currents and winds, and the six small, white shells represent islands".
-

Captain Scott writes in his den in the Terra Nova hut in this October 7, 1911.
-

"The Hunting of the Snark offers a timely caution for geographical investigation. The danger, both academic and pragmatic, of enslavement to static conceptual categories, rigid classifications, and established methodological procedures is simply that they tend to rule out the possibility of experiencing that insight and understanding which can be neither discovered, formulated nor communicated by adherence to traditional investigative methdologies. This is not to advocate an un-methodical and irrational geographical philosophy, but rather to suggest that there may be conditions under which slavish adherence to a tried and tested methodology may fail to provide reliable guidance in our search for understanding. A lack of commitment to open-ended investigation could mean that, because our methods are inappropriate, our explorations will forever remain, so to speak, 'snarked' ".
-

"He had bought a large map representing the sea, Without the least vestige of land: And the crew were much pleased when they found it to be A map they could all understand".
-

Marseille, France: A resident of a block of flats is passed food by his neighbours using a rope made of blankets.
-

Installation. Material provided by family and friends.
As of 08/18/2009, Moor is 326.9 feet long (99.63 meters). Moor will continue to grow.
-

Installation. Material provided by family and friends.
As of 08/18/2009, Moor is 326.9 feet long (99.63 meters). Moor will continue to grow.
-

Addressing the fact that 95% of known animal species are smaller than our thumbs, yet natural history museums displays are filled with mostly large animals, this sub-museum shows the legs of a flea highlighting its muscles; a whole squid, just a couple of millimetres long; beetles that have been sliced along their entire length, through the antennae, head, legs and body — 1/10th of a millimetre thick; as well as these two baby flounder fish.
-

"With a crowd of pilot fish he prowled around the raft, and went on doing this for so long that that we plucked up courage. And when he lay to under the steering oar to scratch his back a bit, we thumped him in return, in a friendly way rather than otherwise, to see how he took it. But he liked it and came back and let himself be thumped three of four times. Then we gave him a bit of a jab with a harpoon, but we ought to not have done that, for he didn't like it and cleared off" (Hesselberg 1950: 48).
-

Whale sharks (Rhincodon typus) are the largest shark, and indeed largest of any fishes alive today. These gentle marine giants roam the oceans around the globe, generally alone. They only feed on plankton. In the Norwegian explorer, Thor Theyerdal's account of his journey by raft across the Pacific Ocean from South America to the Polynesian islands in 1947, the crew is visited by one of these curious and benign creatures:
"In reality the whale shark went on encircling us for barely an hour, but to us the visit seemed to last a whole day. At last it became too exciting for Erik, who was standing at a corner of the raft with an eight-foot hand harpoon, and, encouraged by ill-considered shouts, he raised the harpoon above his head. As the whale shark came gliding slowly toward him and its broad head moved right under the corner of the raft, Erik thrust the harpoon with all his giant strength down between his legs and deep into the whale shark’s gristly head. It was a second or two before the giant understood properly what was happening. Then in a flash the placid half-wit was transformed into a mountain of steel muscles. We heard a swishing noise as the harpoon line rushed over the edge of the raft and saw a cascade of water as the giant stood on its head and plunged down into the depths. The three men who were standing nearest were flung about the place, head over heels, and two of them were flayed and burned by the line as it rushed through the air. The thick line, strong enough to hold a boat, was caught up on the side of the raft but snapped at once like a piece of twine, and a few seconds later a broken-off harpoon shaft came up to the surface two hundred yards away" .
-

After initially making good progress, Terra Nova expedition party’s prospects steadily worsened as they struggled northward. Deteriorating weather, frostbite, snow blindness, hunger and exhaustion led to Edgar Evans dying on 17 February and Lawrence Oates, whose condition was aggravated by an old war-wound to the extent that he was barely able to walk, voluntarily leaving his tent on 16 March and walking to his death. (“I am just going outside and may be some time".)" (Liebenberg 2011: 75).
-

Robert Falcon Scott’s Terra Nova expedition reached the South Pole on 17 January 1912 — 23 days too late. Inside a small tent supported by a single bamboo flying a Norwegian flag, was a record of the five who had been the first to reach the pole: Roald Amundsen, the leader, and his team - Olav Olavson Bjaaland, Hilmer Hanssen, Sverre H. Hassel and Oscar Wisting.
On 19 January, they began their 1,300 kilometre journey home, Scott writing: “I’m afraid the return journey is going to be dreadfully tiring and monotonous” (Scott 1914: 548).
-

A showcase of fish found in the Artic regions.
-

A label in the Natural History Museum accompanying a discovery made by Mary Anning.
-

"Our hands resemble fossil fins; our heads are organised like those of long extinct jawless fish and major parts of our genomes still look and function like those worms and bacteria" (Shubin 2008).
During the summer of his second year of study, paleontologist and evolutionary biologist, Neil Shubin, discovered a particular fossil fish in the Arctic, naming it the Tiktaalik. In Your Inner Fish: A Journey into the 3.5-Billion-Year History of the Human Body (2009) he explored the connections in our human anatomy with those fishes that ventured onto land over 375 million years ago, based on the information gathered from studying the Tiktaalik.
-
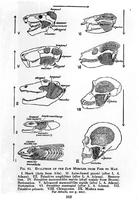
The evolution of jaw muscles from fish to men.
-

A label accompanying Robert Louis Stevenson's fishing gear.
-

"Dear Doctor Barnard
I am an 11 year old girl, and I have a problem: I went fishing today; when we came back, my parents cleaned the fish, and after they took out the insides, they found a heart of a fish beating, but the fish was dead and cut up. It was still beating for about 1/2 an hour. Can you explain that? I am very interested in biology, and so is everyone else in my family.
Sincerely Yours,
Lillian Levy
P.S. I know you are a very busy man, but, if you have enough time, please try to answer. THANK YOU!
P.P.S. If a doctor says you're dead and they take out your heart but it is still beating, are you dead or alive?"
Transcribed letter from the Heart of Cape Town Museum
-

Fishing rods over a bridge in Istanbul.
-

"The BWC shop was located a short walk from Walter Floyd’s dental practice which he bought in 1904 (for £2,404 16s 8d) and shared with his partner, William Johnston. It is uncertain when Floyd first came out to South Africa, but records prove that he was living here by January 1902 (Hart & Lydall, 1981: 1)" (Liebenberg 2021: 52).
In interviews with Mary Floyd in 2015, I showed her this photo of her father-in-law on the boat, en route to Cape Town, and asked her whether she knew who the woman in the photo was. (She appeared in quite a few photos of Floyd's from this period – one especially intimate one showing her lying on a beach and smiling coyly at the photographer.) Was it Agnes, perhaps? She said it definitely wasn't.
-

"When it (the chest) is not being exhibited in the Iziko South African Museum, it lives in the archives of the University of Cape Town. As part of an institution that has sworn dedication to decolonising its curriculum, it poses a somewhat latent threat. In a speech in 2015, the writer and previous vice-chancellor of the University of Cape Town, Professor Njabulo Ndebele, stated "that there can be no transformation of the curriculum, or indeed of knowledge itself, without an interrogation of archive". It is an argument which strongly suggests that a critical assessment of the archival legacy on which the institution is founded becomes of pivotal importance when developing a decolonial institution.
What worth then, if any, does this dormant object serve in a new curriculum?"
Extract from a paper delivered at the BSHS conference in Cambridge, 2019
-

"All that debris still remains under the bridge for the most part, and it has become a dive site. It is a very difficult dive site to get to because of the swiftly moving water and the very short period of slack time.
Nature in this area has just a tremendous ability to take over. You have a man-made structure like the Tacoma Narrow Bridge that collapsed into the water. Very quickly, the ocean took it over and made it part of the habitat".
Extract from the voiceover of trailer for 700 Feet Down (a documentary about the Tacoma Narrows Bridge told through witnesses of the bridge’s 1940 demise as well as intrepid divers exploring a reef of wreckage, ultimately reflecting on how history influences the present)
-

"As I stood there, suddenly, no, not suddenly, but in a sort of driving heave, the whole sea surged, it was not a wave, but a smooth rolling swell that seemed to come up from the deeps, as if something vast down there had stirred itself, and I was lifted briefly and carried a little way toward toward the shore and then set down on my feet as before, as if nothing had happened. And indeed nothing had happened, a momentous nothing, just another of the great world's shrugs of indifferennce (Banville 2005: 26)
-

A year after Simone's death from cancer, Cousteau announced that he had been having an affair with a woman, Francine Triplet, for over a decade. He also had two children with her, Diane and Pierre-Yves.
-

An IV drip releases a drop on a handkerchief floating above a fan, drying it before next one falls.
-

A monumental installation piece recreating the ocean liner Titanic as a floating deck plan (in its original size – 882 feet long; 92 feet wide), projected in light onto the surface of the Hudson River at Pier 59 (due west of West 18th Street), the ship's intended destination in 1912.
-

In a short story by the writer Alice Munro titled, 'Walker Brothers Cowboy', a young girl joins her father, a fox farmer turned traveling salesman, on his visits to homes in the countryside where they live. After observing her father nearly getting doused with a chamber pot of urine by an unwelcoming customer, he veers off his usual rounds to visit a woman whom she slowly understands to be his sweetheart from when he was younger. Driving back home, she thinks about the events of the day:
"So my father drives and my brother watches the road for rabbits and I feel my father's life flowing back from our car in the last of the afternoon, darkening and turning strange, like a landscape that has an enchantment on it, making it kindly, ordinary and familiar while you are looking at it, but changing it, once your back is turned, into something you will never know, with all kinds of weathers, and distances you cannot imagine.
When we get closer to Tuppertown the sky becomes gently overcast, as always, nearly always, on summer evenings by the Lake" (Munro 2010: 23).
-

Newspaper article about Walter Floyd's death
-

My dear Barrie,
We are pegging out in a very comfortless spot. Hoping this letter may be found and sent to you, I write a word of farewell.... More practically I want you to help my widow and my boy – your godson.
(...)
I am not at all afraid of the end, but sad to miss many a humble pleasure which I had planned for the future on our long marches. I may not have proved a great explorer, but we have done the greatest march ever made and come very near to great success. Goodbye, my dear friend.
Yours ever,
R. Scott.
(Excerpt from letter penned by Scott to Barrie on 29 March 1912)
-

Metronome, fishing hook, sinker, crimp and laboratory clamp.
The fishing sinker supplies a counter weight, which allows ticking to continue even though the metronome is suspended upside down. The weight is however, exercising a force which will inevitably exhaust the metronome spring, causing it to cease functioning.
-

"Just about dusk one day in April 1948 Ed Ricketts stopped work in the laboratory in Cannery Row. He covered his instruments and put away his papers and filing cards. He rolled down the sleeves of his wool shirt and put on the brown coat which was slightly small for him and frayed at the elbows.
He wanted a steak for dinner and he knew just the market in New Monterey where he could get a fine one, well hung and tender. He went out into the street that is officially named Ocean View Avenue and is known as Cannery Row. His old car stood at the gutter, a beat-up sedan. The car was tricky and hard to start. He needed a new one but could not afford it at the expense of other things.
Ed tinkered away at the primer until the ancient rusty motor coughed and broke into a bronchial chatter which indicated that it was running. Ed meshed the jagged gears and moved away up the street.
He turned up the hill where the road crosses the Southern Pacific Railways track. It was almost dark, or rather that kind of mixed light and dark which makes it very difficult to see. Just before the crossing the road takes a sharp climb. Ed shifted to second gear, the noisiest gear, to get up the hill. The sound of his motor and gears blotted out every other sound. A corrugated iron warehouse was on his left, obscuring any sight of the right of way.
The Del Monte Express, the evening train from San Francisco, slipped around from behind the warehouse and crashed into the old car. The cow-catcher buckled in the side of the automobile and pushed and ground and mangled it a hundred yards up the track before the train stopped" (Steinbeck 1951: 279).
After Ricketts' death in 1948, Steinbeck dropped the species catalogue from the earlier 'The Sea of Cortez' and republished it with a eulogy to his friend added as an afterword.
-

St. Pancras Station, London.
Suitcases full of holes, handkerchiefs and string sculpture - destroyed by the train pulling out of the station
-

Extract from J.D. Salinger's 'For Esmé - With Love and Squalor' in which Seymour Glass interacts with a young girl while swimming in the ocean on holiday.
“Miss Carpenter. Please. I know my business,” the young man said. “You just keep your eyes open for any bananafish. This is a perfect day for bananafish.”
“I don’t see any,” Sybil said.
“That’s understandable. Their habits are very peculiar.” He kept pushing the float. The water was not quite up to his chest. “They lead a very tragic life,” he said. “You know what they do, Sybil?”
She shook her head.
“Well, they swim into a hole where there’s a lot of bananas. They’re very ordinary-looking fish when they swim in. But once they get in, they behave like pigs. Why, I’ve known some bananafish to swim into a banana hole and eat as many as seventy-eight bananas.” He edged the float and its passenger a foot closer to the horizon. “Naturally, after that they’re so fat they can’t get out of the hole again. Can’t fit through the door.”
“Not too far out,” Sybil said. “What happens to them?”
“What happens to who?”
“The bananafish.”
“Oh, you mean after they eat so many bananas they can’t get out of the banana hole?”
“Yes,” said Sybil.
“Well, I hate to tell you, Sybil. They die.”
“Why?” asked Sybil.
“Well, they get banana fever. It’s a terrible disease.”
“Here comes a wave,” Sybil said nervously.
“We’ll ignore it. We’ll snub it,” said the young man. “Two snobs.” He took Sybil’s ankles in his hands and pressed down and forward. The float nosed over the top of the wave. The water soaked Sybil’s blond hair, but her scream was full of pleasure.
With her hand, when the float was level again, she wiped away a flat, wet band of hair from her eyes, and reported, “I just saw one.”
“Saw what, my love?”
“A bananafish.”
“My God, no!” said the young man. “Did he have any bananas in his mouth?”
“Yes,” said Sybil. “Six.”
The young man suddenly picked up one of Sybil’s wet feet, which were drooping over the end of the float, and kissed the arch.
“Hey!” said the owner of the foot, turning around.
“Hey, yourself! We’re going in now. You had enough?”
“No!”
“Sorry,” he said, and pushed the float toward shore until Sybil got off it.
He carried it the rest of the way.
(Salinger 1986: 20-21).
-

A live phone line was created to an Icelandic glacier, via an underwater microphone submerged in Jökulsárlón lagoon, an outlet of Vatnajökull. The number 07757001122 could be called from any telephone in the world, and the listener would hear the sound of the glacier melting.
-

"One of Hans Haacke’s earlier works. While over time the artist developed a critique of art as an institution and system, these early works focus on art in the sense of process and physical system. Interested in biology, ecology and cybernetics, in the mid-sixties Haacke was influenced by the ideas of Ludwig von Bertalanffy, especially those outlined in his General System Theory of 1968. For the Austrian biologist and philosopher, a living organism is an open system that continuously changes depending on its dialogue or interaction with the environment. Haacke’s early works, such as Condensation Cube, transpose this concept to the realm of art" (MACBA 2021).
-

Photo of water in Jagger Library by photographer, Lerato Maduna.
On 18 April, the Jagger Library — the medicine chest's home — caught fire. The fire started on the lower sections of Rhodes Memorial at the foot of Table Mountain, and set alight landscape, monuments, and many of the university’s buildings. The library only caught fire in the late afternoon, but became a raging inferno as books, artworks, manuscripts that were worked on frequently, institutional, and administrative records of Special Collections, as well as the entire African Film collection, all went up in flames.




















































