Items
Is Part Of is exactly
Centre for Infectious Disease Epidemiology and Research
-

Chest: a botanical ecology
Illness and disease affect us all. The treatment of these conditions however, has been vast and varied, depending on the historical periods and the cultural context in and during which they are practiced. Situated in the rock art gallery, where healing power is expressed in San paintings, this mobile set of cabinets explores a rich complex of healing practices through the display of a medicine chest which was donated to the university of Cape Town in 1978. This chest belonged to a British dentist, who practiced in Cape Town from 1904, and who bought the chest for a hunting trip he undertook in 1913 to (then) Northern Rhodesia. The idea of the chest then gives rise to a variety of forms of healing: from instruments used to exorcise evil spirits and children's letters written to celebrate a heart transplant; to medicinal flowers bought at the Adderley Street flower market. The exhibition aims to visualise and materialise illness and its treatment from historical, cultural and disciplinary perspectives. Drawing on well-established historical and contemporary connections between the disciplines of Botany, Medicine and Pharmacology, the exhibits also suggest latent links which are at times political, at times whimsical. -

First Aid: Homage to Joseph Beuys
This work by the artist, Susan Hiller, consists of 13 vintage felt-lined wooden first aid boxes, 86 vintage bottles, water from holy wells and sacred streams, and vintage medical supplies. -

Livingstone
A small wooden chip from the same object collection as the medicine chest balanced on top of one of the bottles from the chest. "The treatment, the Livingstone rouser, was formulated by Dr Livingstone, who, after an attack of malaria in 1853, patented this mixture of quinine and purgatives (calomel, rhubarb and jalop) mixed with opium (Barrett & Giordani 2017: 1655–1666). The chip balanced on its lid is said to be from the almond tree under which he proposed to Mary Moffat in 1844. The juxtaposition of these two objects, one representing the quantifiable and the other the poetic, draws the viewer to consider the conflation of these two realms" (Liebenberg 2021: 273). -

Healing instruments
“I invited Edmund February to the Kirby collection to view the instruments and learn his thoughts on them from a botanical perspective. February identified the dancing rattles as being made of the seed pods of Oncoba spinosa (Venda: mutuzwa) and the seed pod of Adansonia digitata (Venda: muvhuyu). The wood of the iodophone was, however, unrecognisable as a result of its handling. February also contacted colleagues in the Department of Zoology and the School of Mathematical & Natural Sciences at the University of Venda, who connected me to a Venda diviner, Muanalo Dyer, who uses similar baobab rattles (and other materials from that tree) in her healing practices. This interdisciplinary engagement showed that these instruments, supposedly frozen in their early 20th century understanding of being on the brink of extinction, remained very much functional in the present” (Liebenberg 2021: 271). -

Listen Laennec
"In this work, the temperature graphs of individuals suffering from malaria, yellow fever, trypanosomiasis and tickborne-relapse fever – all viewed as ‘tropical’ and treatable by the contents of the medicine chest – were converted into a musical score. I punched the strips of paper of a hand-cranked musical box mechanism with holes that corresponded to the graphs – the vertical axis representing temperature variations and the horizontal axis representing the approximate number of days the fever is said to last. The translation of these graphs into notes seems nonsensical, as we do not listen for a temperature; we measure it by feeling a forehead or taking a reading with a thermometer. The practice of listening has, however, been part of the history of medicine since the days of Hippocrates (c.460–c.370 BC), when physicians performed auscultations of the lung and heart by placing their ear directly on the patient’s chest' (Liebenberg 2021: 265). -

A 'Jungle'
"A ‘jungle’ consisted of a selection of pathological specimens from the Pathology Learning Centre that had been affected by typhoid fever, ascaris adult worms, yellow fever, amoebic ulcerations, tuberculosis and malaria. The diseases that afflicted these specimens were regarded as ‘tropical’. As described in Chapter One, BWC used the jungle as a significant terrain that called for a medicine chest to combat pathogens: ‘Whether you were valiantly saving your compatriot in war, traversing a dark African jungle, navigating one of the world’s first flying machines, exploring the most desolate place on earth, ascending the highest mountain in the world, or simply enjoying the windswept British coast, the chest would be there, ready for any ailment’ (Johnson 2008b: 255). BWC promoted their chests as the ideal antidote for a tropical landscape ‘at once full of potential wealth for imperial Britain, but simultaneously rife with disease’ (Johnson 2008b: 258) and claimed that the tropical colonies were ‘by far the most dangerous regions for travellers’ (BWC 1934: 8). It was here that ‘desolating ailments’ were encountered, all ‘particularly fatal to the so-called white man who originates in temperate climates’ (BWC 1934: 8). I adapted the colour of the images of afflicted intestines, livers, stomachs and brains and used them as material to construct a dense jungle that referenced this aspect of the medicine chest’s history. Printed on separate glass sections that fit into the cabinet at spaced intervals to create an illusion of depth and three-dimensionality, the work draws on the cross-sectional display technique used in many anatomy museums worldwide, in projects such as the Visible Human Project (1995) and that the artist Damien Hirst references in his works . Creating a visual link between the UCT specimens and the history of these diseases surfaces the occluded racial undertones of these understandings" (Liebenberg 2021: 267). -

Subtle Thresholds (PLC)
"Integrated into the PLC, these works speak to the specimens on display and provide interesting access points to the collection. The animal-faeces prints (which referenced ‘sites of contamination’ in the context of the SAM exhibition) resonate, for instance, with many of the specimens on display in the PLC, such as the heterotopic heart (also called a ‘piggy-back heart transplant’) created by Dr Chris Barnard in 1977, consisting of a baboon heart grafted onto a human heart for additional motoric support. In addition to their more ‘famous’ specimens, the centre also has an extensive intestinal worm collection and many organs affected by zoonotic diseases, such as a liver ravaged by malaria. This was not a conscious decision on the part of the artist-curator and illustrates how curation can draw attention to aspects of a collection and liberate new associations when brought into conversation with it" (Liebenberg 2021: 201). -

The Kirby collection of musical instruments
"Kirby’s choice of an ‘age-old simple classification’ to order the instruments can be correlated with another classification formulated at Wits around the time he was collecting. The Department of Bantu Studies was established in the 1920s at roughly the same time as the Music Department. Kirby’s use of the phrase ‘native races’, which features in the title of his book, resonates with the descriptive subtitle of the Wits journal connected to research in this department: Bantu Studies: A Journal Devoted to the Scientific Study of Bantu, Hottentot, and Bushman (Nixon 2013: xii). The homogenising act of categorising all diverse indigenous South African groups into three general categories seems to echo Kirby’s taxonomic imposition on the diverse instruments he collected on his trips and that continues to feature as the ordering principle of this collection" (Liebenberg 2021: 136). -
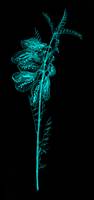
Planthology (detail)
“For 'Planthology (Bulbine frutescens and Lessertia frutescens)' I sourced two medicinal plant specimens from Kirstenbosch National Botanical Garden and x-rayed them at Groote Schuur Hospital (#10 and #13). These two local plants offer a wide variety of healing properties and address the lacuna of the chest. The fresh leaves of the Bulbine frutescens produce a jelly-like juice that can be used for burns, rashes, blisters, insect bites, cracked lips, acne, cold sores, mouth ulcers and areas of cracked skin, while an infusion of these leaves in a cup of boiling water can be taken for coughs, colds and arthritis (Harris 2003: online). The Lessertia frutescens is used as an immune booster in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, as a medicine in the treatment of chicken pox, internal cancers, colds, asthma, TB, bronchitis, rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, liver problems, haemorrhoids, piles, bladder and uterus problems, diarrhoea, dysentery, stomach ailments, heartburn, peptic ulcers, backache, diabetes, varicose veins and inflammation (Xaba & Notten 2003: online)” (Liebenberg 2021: 269). -

Planthology
In conversation with Dr Yeats in 2011 about adding a few medicinal plants to the centre as part of its displays, she mentioned that no plants survived in there. They all seemed to die from some mysterious cause. I decided to source three medicinal plants, the Lessertia frutescens, Bulbine frutescens and Artemisia afra, and X-ray them to 'diagnose' what might be the cause of their demise. In subjecting the plants to this process and placing the x-ray images in a space that foregrounds the diagnosis of human disease, I intended to create a heterarchical shift in this relationship, considering a world in which the degree of care directed toward human ailments might be replicated in treating diseases manifest in the botanical world. -

‘Mrs Glover attending to an ill African chief.’
"The figure of ‘Mrs Glover’, kneeling and treating what appears to be a very ill man, exudes not only the authority of Western medicine within the local context but conveys her as the self-sacrificing and caring European ‘civilizer’ in service of expanding the empire, ‘the medicine chest conveniently by her side’ (Johnson 2008b: 259)" (Liebenberg 2021: 63 - 65). -

Hoard
"The chest was featured in a work titled 'Hoard', for which Bloch sculpted in clay the objects in the UCT collection as well as ones from the 11th century Mapungubwe collection (housed at the University of Pretoria). She painted these sculpted objects gold and presented them in museum display cases, drawing attention to the arbitrary nature of objects’ value and to the possibility that historically loaded items can be accidentally overlooked and misevaluated (Bloch in Honigman 2014: online)" (Liebenberg 2021: 82 - 84). -

Hosts and Carriers
A selection of glass slides of the insects, ticks and worms that are the primary or intermediate hosts or carriers of human diseases. These slides also featured in the 'Curiosity CLXXV' and 'Subtle thresholds' exhibitions, sourced from the Pathology Learning Centre (PLC), where they were originally donated by the secretary of the Department of Microbiology. Dr Yeats identified them as glass photomicrographs and speculated that they were probably made for a special projector used for teaching many years ago. -

Clivia's in Kirstenbosch
Part of the ‘Useful plants’ section at Kirstenbosch National Botanical Garden. -

Rattles in the Kirby collection
A drawer of rattles in the South African College of Music's Kirby collection: "The instruments are now grouped in different cabinets according to the taxonomy set out by Kirby in his book. In the preface to the second edition (1964), Kirby shares some of his considerations when deciding how to group the instruments, writing that he had to decide ‘whether to arrange his material tribally, or to deal with each type of musical instrument separately from the technological and historical points of view, allowing the tribal aspects to emerge incidentally’ (Kirby 1964: xi). Kirby chose the second alternative, stating that his chief reason was that he wanted the work to be, as far as possible, ‘a complete and comparative study of one particular aspect of the life of our aborigines’ (1964: xi). His second consideration was to find the most suitable manner for classifying the instruments, for which he defaulted to the ‘age-old simple classification of musical instruments into three main groups of percussion, wind and strings’ (1964: xi) – a Western system for the classification of instruments and the principles on which they were based. The chapters in his book and the displays in the room are thus grouped into three categories: percussion – ‘rattles and clappers’, ‘drums’, ‘xylophones and sansas’ and ‘bull-roarers and spinning-disks’; wind instruments – ‘horns and trumpets’, ‘whistles, flutes, and vibrating reeds’ and ‘reed flute ensembles’; and stringed instruments – ‘stringed instruments’ and ‘Bushmen and Hottentot violins and the ramkie’. Kirby encountered one taxonomic anomaly when employing this system: the ‘gora’, an instrument both wind and string, which he termed ‘a stringed-wind instrument’" (Liebenberg 2021: 135). -

A1.44.
The contents of Floyd’s two travelling cases for his hunting trip (BC666 A1.44. Special Collections, University of Cape Town). -

BWC Cape Town premises
"When Burroughs died of pneumonia in 1895, Wellcome became BWC’s sole owner, and the next 20 years (until the outbreak of World War I) constituted a period of massive expansion for the company (Bailey 2008: online). In 1898, the first overseas branch opened in Sydney and was followed by seven more branches – in New York, Montreal, Buenos Aires, Cape Town, Milan, Shanghai and Bombay – by 1912. The Cape Town branch opened in 1902, seven years after Wellcome made his first visit to the city in 1895" (Liebenberg 2021: 49 - 51). -

BWC Cape Town premises (drawing)
Line drawing of the Burroughs Wellcome & Co. office, Cape Town, South Africa. -

Corrections
Examples of Wellcome's design changes annotated on tracing paper. 1914–1938. WF/M/I/PR/O01/3, 4, 9, 8. Wellcome Collection. -

BC666
A page of the Tabloid guide. -
'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

Wednesday, 1 April 2020
Marseille, France: A resident of a block of flats is passed food by his neighbours using a rope made of blankets. -

The virus (dormant)
"When it (the chest) is not being exhibited in the Iziko South African Museum, it lives in the archives of the University of Cape Town. As part of an institution that has sworn dedication to decolonising its curriculum, it poses a somewhat latent threat. In a speech in 2015, the writer and previous vice-chancellor of the University of Cape Town, Professor Njabulo Ndebele, stated "that there can be no transformation of the curriculum, or indeed of knowledge itself, without an interrogation of archive". It is an argument which strongly suggests that a critical assessment of the archival legacy on which the institution is founded becomes of pivotal importance when developing a decolonial institution. What worth then, if any, does this dormant object serve in a new curriculum?" Extract from a paper delivered at the BSHS conference in Cambridge, 2019 -

Simone
A year after Simone's death from cancer, Cousteau announced that he had been having an affair with a woman, Francine Triplet, for over a decade. He also had two children with her, Diane and Pierre-Yves. -

Untitled
An IV drip releases a drop on a handkerchief floating above a fan, drying it before next one falls. -

Wave
Screengrab of an image search, typing in 'third wave' -

Devils Bridge sketched by Lister
'Devils Bridge' sketched by Lister on his travels through Europe showing a bridge crossing the Gotthard Pass, northern approach, Switzerland. The term 'devil's bridge' is applied to many ancient bridges found primarily in Europe. These were stone or masonry arch bridges and, because they represented a significant technological achievement in ancient architecture, were objects of fascination and stories. The most popular of these featured the Devil, either as the builder of the bridge (relating to the precariousness or impossibility of such a bridge to last or exist in the first place) or as a pact-maker (sharing the necessary knowledge to build the bridge, usually in exchange for the communities souls). The legend attached to the bridge sketched by Lister is of the latter, and was related by Johann Jakob Scheuchzer in 1716. According to Scheuchzer, the people of Uri recruited the Devil for the difficult task of building the bridge. In return for his expertise, the Devil requested the soul of the first thing to pass the bridge. To trick the Devil, the people of Uri sent across a dog by throwing a piece of bread, and the dog was promptly torn to pieces by the Devil. Reference: Scheuchzer, J. , 1747 [1716]. Naturgeschichte des Schweitzerlandes. Vol. 2: 94. -

Observing marbling in Edirne
A marbling demonstration observed during a 2012 trip to Istanbul and a visit to the neighbouring Edirne's Health Museum. Opened in Sultan Bayezid II külliye in 1488, the hospital treated patients for over 400 years, until 1909, along the tradition of Turkish-Islamic medicine, which included the treatment of diseases by music. -

Lacuna (Part one)
"It is interesting to note that the botanical origins of most of these medicines were from outside of Africa, especially if one considers the long history of the Cape as a point on the trade routes where ill sailors regularly disembarked and drew on the knowledge of the Khoekhoe traditional healers for treatment and herbal cures (Laidler & Gelfand 1971: 44). The Cape flora offered a plenitude of medicinal resources and these healers (who were skilled in botany, surgery and medicine) used them in a variety of healing practices . The exclusion of local botanical remedies in the BWC No. 254 medicine chest can be attributed to many factors" (Liebenberg 2021: 67). -

The broken tulip
"During the period known as tulipmania which transpired in the Netherlands during the 17th century, contract prices for bulbs of the recently introduced tulip reached extraordinarily high levels and then suddenly collapsed. Tulips that displayed a break in their colour reached prices far higher than those that didn’t. It wasn’t until 1920, after the invention of the electron microscope, that scientists discovered that the cause for this symphony of colour was a virus that spread from tulip to tulip by Myzus persicae, the peach potato aphid. Michael Pollan in The Botany of Desire, explains this phenomenon: “The colour of a tulip consists of two pigments working in concert — a base colour that is always yellow or white and a second, laid-on colour called an anthocyanin; the mix of these two hues determining the unitary colour we see. The virus works by partially and irregularly suppressing the anthocyanin, thereby allowing a portion of the underlying colour to show through — creating the magic of the broken tulip. A fact that, as soon as it was discovered, doomed the beauty it had made possible" (Pollan 2003: 97 in Liebenberg 2011: 92). -

Semper Augustus Tulip
Photo of Semper Augustus watercolour, captured whilst perusing the Pera Museum, Istanbul, 2013 -

Tobacco Mosaic Virus
During the late 19th century, tobacco farmers observed a strange occurrence on the leaves of their tobacco plants. A mosaic pattern of light and dark green (or yellow and green, in some instances) appeared on the leaves of their crops, the presence of which signalled the steady decline in the plant’s growth. Because of the lucrative nature of the industry, finding a treatment for this seemingly infectious disease became a priority, with many laboratories working to isolate the cause. Bacteria were recognised as the causative agents of many infectious diseases of plants and animals, including humans, in the second half of the 19th century – and the technique of filtration was developed to separate infectious agents from extracts or exudates in order to study these microbes. It was whilst utilising this technique that Dmitri Ivanovski, a Russian microbiologist working in the Crimea in 1890, made a surprising discovery. Using the Chamberland–filter made from porcelain and designed to trap ordinary bacteria, Ivanovsky discovered that the filtered sap from the diseased plants could continue to transfer the infection to healthy plants – an occurrence he attributed to an agent which must be an exceedingly small parasitic microorganism, invisible even under great magnification. It would take another 45 years before the visualisation of this subcellular entity would be formulated with the help of an electron microscope, but Ivanovksy, along with the Dutch botanist M.W. Beijerinck, who also and independently, isolated these microbes in his laboratory in 1898, are generally credited for the discovery of viruses. The disease which infected the tobacco plants would be aptly called the Tobacco Mosaic Virus, and its identification would signal the initiation of a field of study known as virology. -

Wings
512 lasercut hands derived from images of healing: 2500 BC - 2000 AD. -
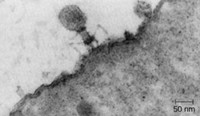
Holes
A virus attacks a cell by attaching itself to the outer wall. It then uses a specialized protein to digest a small hole in the wall of the cell and inject its nucleic acid molecule into the cell's cytoplasm. -

Icarus
Perspex wings with histology slides. Histology slides are prepared by taking a sample of biological tissue and fixing it to preserve the tissue in as natural a state as possible and prevent postmortem decay. The tissue is immersed in a chemical fixative and then embedded in wax to make it hard enough to cut into very thin sections of tissue (usually 5 to 7 micrometers in thickness). It is then passed through baths of solvents which remove the wax, then through graded alcohols, water and finally through baths of haematoxylin and eosin to stain it for better viewing under a microscope. -

Soda-Mint (Neutralising)
"Antacid, exhilarant and stimulant. From one to three as a neutralising agent, in irritable and acid conditions of the stomach, dyspepsia, flatulence, etc. They may be swallowed with water, or be powdered and dissolved in water and taken as a draught" (BWC 1925:138). -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (Back cover)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (End pages)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p148)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p146,147)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p144,145)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p142,143)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p140,141)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p138,139)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p136,137)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p134,135)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p132,133)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p130,131)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p128,129)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p126,127)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products


