Items
Is Part Of is exactly
Special Collections
-

Livingstone
A small wooden chip from the same object collection as the medicine chest balanced on top of one of the bottles from the chest. "The treatment, the Livingstone rouser, was formulated by Dr Livingstone, who, after an attack of malaria in 1853, patented this mixture of quinine and purgatives (calomel, rhubarb and jalop) mixed with opium (Barrett & Giordani 2017: 1655–1666). The chip balanced on its lid is said to be from the almond tree under which he proposed to Mary Moffat in 1844. The juxtaposition of these two objects, one representing the quantifiable and the other the poetic, draws the viewer to consider the conflation of these two realms" (Liebenberg 2021: 273). -

Etching from 'Sound from the Thinking Strings'
"Skotnes’s own visual interpretation of the history and cosmology of the |xam formed the last component of this interdisciplinary endeavour and constituted a visual component that drew together the various strands of disciplinary interpretations and presented a perspective on the |xam life she felt ‘was missing from the other interpretations’ (Skotnes 1991: 30). In these images she drew freely on San mythology, accounts of |xam life recorded by Lucy Lloyd, historical and archaeological research and images from rock paintings in a landscape setting. She writes in her preface that these etchings were direct attempts at ‘inverting the museum dioramas’ in the ethnographic halls close to the exhibition and which, through their display of the San’s body casts, rendered them closer to specimens of biology than as members of a highly developed culture (Skotnes 1991: 52). By creating images that combined shamanistic rituals, entoptic spirals, plants, hunting bags, bows and arrows, snakes, eland-shaped rainclouds, colonists, musical instruments, shelters and therianthropic shapes, Skotnes eclipsed the static narratives of the dioramas and the object labels in the exhibition, placing them in a context in which their metaphysical qualities were celebrated more than their physical qualities. These prints stood in striking contrast to the other exhibits, which framed the San as physical types, and they challenged viewers to confront the reality that the San had a rich history and cultural and social life" (Liebenberg 2021: 157). -

Sound from the Thinking Strings (installation detail)
"Skotnes had a longstanding relationship with the museum, which started when she was still a student at the Michaelis School of Fine Art. Davison remembers that Skotnes would visit the taxidermy section of the South African museum to draw bones. As an anthropologist, Davison admits to finding Skotnes’s way of looking at things stimulating – an individual way of looking at objects that made her look at them differently, even though she was already very familiar with these materials. Davison recalls a visit to the ethnographic stores during which she showed Skotnes the San skin bags, carefully conserved in their drawers and laid out on acid-free paper. Skotnes admired not only their aesthetic qualities but related the stories she had been studying in the Bleek and Lloyd archive to them – stories that shifted their status from anthropological museum objects to powerful animate objects in San spiritual and social life (P. Davison, personal communication, 28 January 2021). Skotnes remembers that she asked staff whether they knew what was inside the bags and was shocked when nobody could remember looking in them. She was allowed to look inside one and found a claw, which they thought must be a leopard’s (P. Skotnes, personal communication, 9 May 2021)" (Liebenberg 2021: 2015). -

Hoard
"The chest was featured in a work titled 'Hoard', for which Bloch sculpted in clay the objects in the UCT collection as well as ones from the 11th century Mapungubwe collection (housed at the University of Pretoria). She painted these sculpted objects gold and presented them in museum display cases, drawing attention to the arbitrary nature of objects’ value and to the possibility that historically loaded items can be accidentally overlooked and misevaluated (Bloch in Honigman 2014: online)" (Liebenberg 2021: 82 - 84). -

A display on page 97 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue
"A stainless-steel dilator from the Drennan collection, a carded set of glass slides of xenopus heart sections from the Medical Microbiology collection, a 19th century game called 'Frogs and Toads' from Special Collections and a wax model of an embryo, also from Drennan. This ‘amphibian’-inspired display showcases many qualities of the curatorial method, such as visual quotation (the combination of these materials foregrounds that the shape of the dilator resembles a frog), analogy (the wax embryo, dilator and frogs allude to the resemblance between sperm and tadpoles) and juxtaposition (the frog as a scientific topic dissected and contained in the slides, and the frog as a board piece in a game played by children)" (Liebenberg 2021: 183). -

A1.44.
The contents of Floyd’s two travelling cases for his hunting trip (BC666 A1.44. Special Collections, University of Cape Town). -

The Landis Museum
A drawing by the artist-curator James Hutchinson (Chapter Thirteen) based on an audio description of the object as art of the Glasgow International Arts festival. "Nina Liebenberg also undertakes a form of object analysis at an institutional border. She spent an afternoon in the strongroom of the University of Cape Town's special collections department, examining an early 20th century medicine box commissioned for a hunting trip in (then) Northern Rhodesia. Such boxes had been essential parts of the British colonial project, and allowed emigres, missionaries and explorers to venture deeper into unknown territory without fear of contracting tropical diseases. Liebenberg’s report from the strongroom acts as a set of instructions for The Landis Museum’s curator to make a drawing of the box, to which he has no physical access". Extract from the 'Exhibition Guide' of the Landis Museum (Chapter Thirteen), Glasgow International Arts Festival, 20 April - 07 May 2018. -

BC666
A page of the Tabloid guide. -
'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

Walter Floyd arrives by boat
"The BWC shop was located a short walk from Walter Floyd’s dental practice which he bought in 1904 (for £2,404 16s 8d) and shared with his partner, William Johnston. It is uncertain when Floyd first came out to South Africa, but records prove that he was living here by January 1902 (Hart & Lydall, 1981: 1)" (Liebenberg 2021: 52). In interviews with Mary Floyd in 2015, I showed her this photo of her father-in-law on the boat, en route to Cape Town, and asked her whether she knew who the woman in the photo was. (She appeared in quite a few photos of Floyd's from this period – one especially intimate one showing her lying on a beach and smiling coyly at the photographer.) Was it Agnes, perhaps? She said it definitely wasn't. -

The virus (dormant)
"When it (the chest) is not being exhibited in the Iziko South African Museum, it lives in the archives of the University of Cape Town. As part of an institution that has sworn dedication to decolonising its curriculum, it poses a somewhat latent threat. In a speech in 2015, the writer and previous vice-chancellor of the University of Cape Town, Professor Njabulo Ndebele, stated "that there can be no transformation of the curriculum, or indeed of knowledge itself, without an interrogation of archive". It is an argument which strongly suggests that a critical assessment of the archival legacy on which the institution is founded becomes of pivotal importance when developing a decolonial institution. What worth then, if any, does this dormant object serve in a new curriculum?" Extract from a paper delivered at the BSHS conference in Cambridge, 2019 -

Sudden death of city dentist
Newspaper article about Walter Floyd's death -

Flood
Photo of water in Jagger Library by photographer, Lerato Maduna. On 18 April, the Jagger Library — the medicine chest's home — caught fire. The fire started on the lower sections of Rhodes Memorial at the foot of Table Mountain, and set alight landscape, monuments, and many of the university’s buildings. The library only caught fire in the late afternoon, but became a raging inferno as books, artworks, manuscripts that were worked on frequently, institutional, and administrative records of Special Collections, as well as the entire African Film collection, all went up in flames. -

A wave crashing
A page from the BWC guide -

Unveiling
A bronze bell with lead clapper. The artist Janine Antoni, asked about this work, stated that she "was thinking of an object that is simultaneously hiding and calling out". -

The Memory of Water
"Of the cases used during Stanley's famous travels, the "Rear Guard" 'Tabloid' Medicine Chest is worthy of special mention. The chest remained in the swamp regions of the Aruwhimi for nearly four years, and more than once was actually submerged in the river. Notwithstanding these mishaps, when the chest was brought back to London and the remaining contents tested by the Official Analyst of the Lancet, they were found to have retained their efficacy "(BWC 1934: 5). -

H.4
This object, a leather cartridge case said to belong to Sammy Marks, occupies a place in the Special Collections of the University of Cape Town. It forms part of the Sammy Marks Papers (BC770). -

A1.21-A1.21.1
An object from BC666: Walter Floyd's physiology notes from when he was a student. -

Chip of wood from an almond tree
Said to be a chip from the tree under which David Livingstone is said to have proposed to Mary Moffat 1884. Wood chip was donated by R.F. Immelman who purchased it from Kimberley museum. -

Floyd in Northern Rhodesia
"In 1913, Walter Floyd undertook a hunting trip with a few of his friends to (then) Northern Rhodesia. It was prior to embarking on this trip, that he purchased the No. 254 medicine chest in the Burroughs Wellcome & Co shop in Cape Town. "With the exception of an occasional Portuguese explorer, the area that became known as Rhodesia lay largely untouched by Western intervention until the mid-19th century. It was only after 1851, when the Scottish missionary and explorer David Livingstone entered this terrain, that accounts of it spread to London and further afield (Taylor 2006: 11). However, a significant number of explorers, missionaries and traders began to arrive in the region after the Berlin Conference (1884–1885) (Simson 1985: 7), and in 1890 Cecil John Rhodes, spearheading British imperial interests in the area, secured, through trickery and deception, exclusive mining concessions from the local chiefs for the British South Africa Company (Taylor 2006: 11). By 1895, the area, now renamed Northern and Southern Rhodesia after Rhodes, was proclaimed a British sphere of influence" (Liebenberg 2021: 57) -

Wounds
A wounded bottle in Special Collections, BC666, UCT -

Holes
A page from the Tabloid guide, BC666, UCT -

Soda-Mint (Neutralising)
"Antacid, exhilarant and stimulant. From one to three as a neutralising agent, in irritable and acid conditions of the stomach, dyspepsia, flatulence, etc. They may be swallowed with water, or be powdered and dissolved in water and taken as a draught" (BWC 1925:138). -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (Back cover)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (End pages)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p148)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p146,147)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p144,145)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p142,143)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p140,141)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p138,139)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p136,137)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p134,135)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p132,133)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p130,131)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p128,129)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p126,127)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p124,125)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p122,123)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p120,121)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p118,119)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p116,117)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -
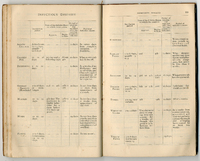
'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p114,115)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p112,113)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -
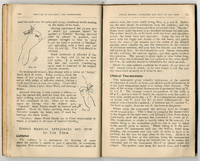
'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p110,111)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p108,109)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p106,107)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p104,105)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p102,103)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products -

'Tabloid' A Brief Medical Guide (p100,101)
A guide to illnesses common to tropical regions and how to cure them using Burroughs Wellcome & Co.'s products


