Items
keywords is exactly
lungs
-

Eucalyptus
"The plants [dislayed in this cabinet] were bought from the Adderley Street flower market in central Cape Town and are used by the sellers for medicinal purposes to treat chest and respiratory problems, with the leaves of the eucalyptus added to a bath and those of the protea infused in hot water and drunk as a broth. The flower sellers trading in Trafalgar Place and along Adderley Street have been doing so since at least the mid-1880s but became viewed as threats to the local flora by the European settlers at about the same time the medicine chest was first introduced to the city at the beginning of the 20th century. The settlers initially preferred to cultivate plants imported from their home countries to indigenous varieties, introducing many species to South Africa for nostalgic or practical reasons (subsequently problematic for local biodiversity) (Van Sittert 2002: 103). In the wake of emerging white nationalism in the 1890s, interest in indigenous plants gained momentum and was deployed to create a sense of belonging to the ‘foreign’ land (Boehi 2013: 133). A botanical discourse was mobilised to underscore ideas about identity and belonging, such as ‘roots’ and ‘ideas of rootedness’, and laws regulating flower picking (which usually occurred on the mountain) were passed in this period and were secured by the Wild Flower Protections Act in 1905 and an amendment thereto in 1908 (Boehi 2013: 133)"(Liebenberg 2021: 275). -

Proteas
"The plants [dislayed in this cabinet] were bought from the Adderley Street flower market in central Cape Town and are used by the sellers for medicinal purposes to treat chest and respiratory problems, with the leaves of the eucalyptus added to a bath and those of the protea infused in hot water and drunk as a broth. The flower sellers trading in Trafalgar Place and along Adderley Street have been doing so since at least the mid-1880s but became viewed as threats to the local flora by the European settlers at about the same time the medicine chest was first introduced to the city at the beginning of the 20th century. The settlers initially preferred to cultivate plants imported from their home countries to indigenous varieties, introducing many species to South Africa for nostalgic or practical reasons (subsequently problematic for local biodiversity) (Van Sittert 2002: 103). In the wake of emerging white nationalism in the 1890s, interest in indigenous plants gained momentum and was deployed to create a sense of belonging to the ‘foreign’ land (Boehi 2013: 133). A botanical discourse was mobilised to underscore ideas about identity and belonging, such as ‘roots’ and ‘ideas of rootedness’, and laws regulating flower picking (which usually occurred on the mountain) were passed in this period and were secured by the Wild Flower Protections Act in 1905 and an amendment thereto in 1908 (Boehi 2013: 133)" (Liebenberg 2021: 275). -

The workshop
"Held in the Department of Human Biology in the Division of Clinical Anatomy and Biological Anthropology, this collection consists of prepared specimens – both bottled and plastinated, anatomical models – and a skeletal repository used for research purposes. The materials are kept in three separate rooms, with the anatomical models in one, the prepared and plastinated specimens in another and the skeleton repository in its own room behind locked doors, viewable by appointment only. The room housing the anatomical models functioned as a workshop when modelmaking was still offered to first year medical students as an elective course: its walls are lined with shelves that display models made from materials ranging from papier-mâché to modern silicon copies and are taxonomised according to their anatomical representations, such as ‘the eye’, ‘head & neck’, ‘dentistry’, ‘embryology’, ‘lungs’ and ‘cardiovascular system’, to name a few. The models represent each anatomical section and are brightly coloured to differentiate the different parts of the human body and aid in identification. Many of the models can be dismantled into separate pieces and, like a puzzle, be reassembled into their original shapes. Interspersed with these models are rolled-up charts depicting organs, bodily systems and anatomical sections of the body in two-dimensional form, as well as old student modelling projects. A selection of animal skeletons is displayed on the far side of the room, and a shelf with a few anatomical specimens in formaldehyde is across from it" (Liebenberg 2021: 121 - 122). -

Weighing Smoke
PAUL That’s the man. Well, Raleigh was the person who introduced tobacco in England, and since he was a favourite of the Queen’s – Queen Bess, he used to call her – smoking caught on as a fashion at court. I’m sure Old Bess must have shared a stogie or two with Sir Walter. Once, he made a bet with her that he could measure the weight of smoke. DENNIS You mean, weigh smoke? PAUL Exactly. Weigh smoke. TOMMY You can’t do that. It’s like weighing air. PAUL I admit it’s strange. Almost like weighing someone’s soul. But Sir Walter was a clever guy. First, he took an unsmoked cigar and put it on a balance and weighed it. Then he lit up and smoked the cigar, carefully tapping the ashes into the balance pan. When he was finished, he put the butt into the pan along with the ashes and weighed what was there. Then he subtracted that number from the original weight of the unsmoked cigar. The difference was the weight of the smoke. TOMMY Not bad. That’s the kind of guy we need to take over the Mets. PAUL Oh, he was smart, all right. But not so smart that he didn’t wind up having his head chopped off twenty years later. (Pause) But that’s another story. -

Second star to the right and straight on 'til morning
Cyanotype on paper. Ink on perspex. The work shows the exact positioning of the stars from J.M. Barrie’s window at 3 Adelphi Terrace, London (51°30'N 0°7'21"W), on Saturday, 19 June 1937 – the night of his death. Based on the direction of his window, I was able to locate the ‘second star to the right’ at the 45 degree angle he would have stood and viewed the night sky. Hopefully, he reached his destination, after departing the flat and traveling ‘straight on till morning’. -

Your inner fish
"Our hands resemble fossil fins; our heads are organised like those of long extinct jawless fish and major parts of our genomes still look and function like those worms and bacteria" (Shubin 2008). During the summer of his second year of study, paleontologist and evolutionary biologist, Neil Shubin, discovered a particular fossil fish in the Arctic, naming it the Tiktaalik. In Your Inner Fish: A Journey into the 3.5-Billion-Year History of the Human Body (2009) he explored the connections in our human anatomy with those fishes that ventured onto land over 375 million years ago, based on the information gathered from studying the Tiktaalik. -
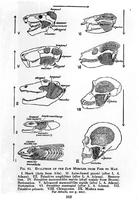
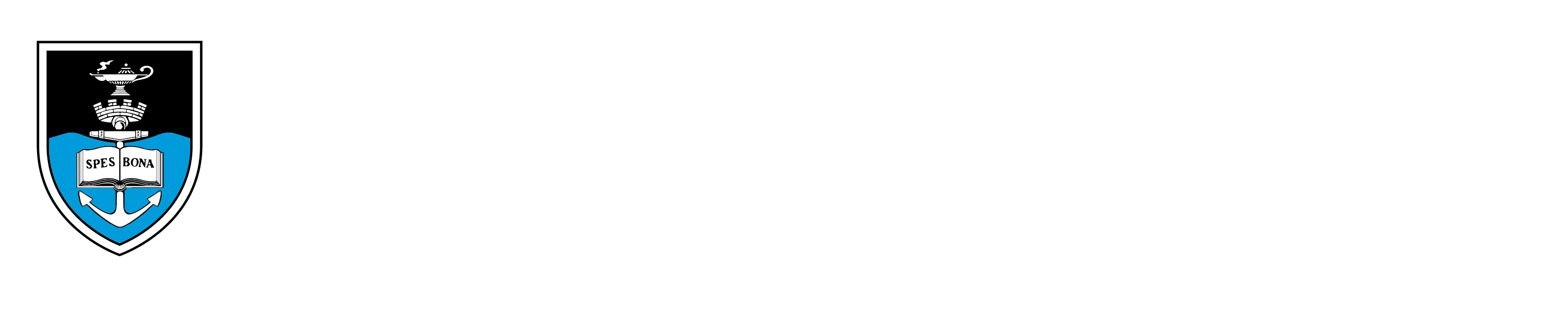
Of fish and men
The evolution of jaw muscles from fish to men. -

Eugen Ransonnet-Villez
"Measuring three feet high by two and half wide and deep, this submersible, of sheet iron and inch-thick glass, had the user's legs sticking out of the bottom so that he could propel himself along the seabed at a depth of five meters or so. It was weighed down by cannonballs, and with air pumped in, the diving bell allowed him to descend for sessions of up to three hours" (The Public Domain Review 2021). -

Lithograph of underwater scene
Lithograph of underwater scene by Eugen Ransonnet-Villez, from colour pencil drawings made by the artist while submerged in his diving bell, from his 'Sketches of the Inhabitants, Animal Life and Vegetation in the Lowlands and High Mountains of Ceylon' (1867) -

Melchior & Cousteau
In 1963 Simone Melchior became the world's first female aquanaut by living in Starfish House, an underwater habitat, for the final four days of the Conshelf II project. Although never visible in the 'Undersea World of Jacques Cousteau' series, Cousteau's wife and business partner played a key role in the operation at sea. She was the acting mother, healer, nurse and psychiatrist to the all-male crew for 40 years. Cousteau describes her as being "happiest out of camera range, in the crow’s nest of the Calypso (...), scanning the sea for whales". Her father, Henri Melchior, was director of Air Liquide (France’s main producer of industrial gases at the time) and funded the invention of the aqua lung and the scuba diving apparatus we know today. -

Kimberley, South Africa: miners and washing gear at the Bultfontein diamond mine
Woodburytype -

Griqualand West, South Africa: Kimberley diamond mine.
Woodburytype -

Kimberley Mine
A detail from the wallpaper used outside the Cape Town Diamond Museum in the V&A Waterfront. -

Kimberley Mine 1886
Plate from Williams, G. 1902. 'The Diamond Mines of South Africa: Some Account of their Rise and Development'. New York, London: Macmillan. -

Haematite Miner's Lung (Or Sidero-silicosis)
Catalogue No: R3-d55-0331. Origin: UCT Anat Path museum. Old Museum No: V:x:6. Year: not recorded. Clinical data: No further clinical or laboratory details are available other than that the patient was an emaciated 50 year old man. Macroscopy: The specimens preserved are both lungs, the heart, kidneys, spleen and and portions of liver. In the thorax, both pleural cavities were completely obliterated by a fibrous pleurisy of long-standing and both lungs were universally adherent throughout. They were stripped off with difficulty and were found to have thickening of the pleura over the upper lobe on the left side and the upper and middle lobes on the right. The lower lobes on both sides were soft and spongy while the upper lobes were dense and firm on palpation but on section there was no cavitation and no evidence of tuberculosis. The left lung showed a dense fibrosis of the whole of the upper lobe and the upper third of the lower lobe; no crepitant lung tissue could be found in the upper lobe while the lower two-thirds of the lower was crepitant and showed emphysema of a hypertrophic nature. The lung was a dull brick colour and haematite dust flowed out with the fluid when the lung was sectioned. The right lung presented a similar appearance to the left. There was a solid dense fibrosis of the upper and middle lobes and the lower lobe showed fibrosis with hypertrophic emphysema. There was no evidence of tuberculosis and on palpation, a dense fibrosis was found with no nodular formation whatever. On section, it showed a similar appearance of a brick-dust colour, dilated bronchi and uniform fibrosis of the upper and middle lobes with no crepitant lung tissue. The pericardial sac was slightly increased in size due to a hypertrophied and dilated heart. The hypertrophy was mostly on the right side and there was a terminal dilatation of the right atrium; the valves and coronary vessels unremarkable.The liver was small and on section showed venous congestion and cloudy swelling. Microscopy: On microscopy, sections of lung show a diffuse fibrosis of both upper lobes with no recognizable lung tissue. The fibrosis in areas has a slightly whorled arrangement, the centre of which is hyaline and contains no iron pigment and surrounding it is a zone of cellular tissue containing masses of iron. In the upper part of the lower lobe where the lung tissue is recognizable as such, a few nodules definitely resembling silica nodules are to be seen. In the both lower lobes a solid oedema was noted and emphysema marked. The fibrosis was not present to anything like the same extent in the lower lobes, the emphysema being the most marked feature. No evidence of tuberculosis was found in either lung, though a calcareous gland was found in the hilum. Under polarised light, the iron showed up as a golden brown with a few points of light, clear, needle-like in contra-distinction to the iron lying free in the fibrous tissue. The macrophages are beautifully shown lying inside the alveoli filled with iron dust. Percentage of Ash 16.6 Percentage of silica to ash 6.6 Percentage of silica to dry lung 1.1 Percentage of iron to ash 10.3 Percentage of iron to dry lung 6.7 Comments: In summary, the post mortem findings were of: Dense pulmonary fibrosis; hypertrophied and dilated right ventricle; failure of compensation. This condition is described as haematite miner's lung or sidero-silicosis, caused by the inhalation of dust containing silica and ferric oxide which is the principal component of the ore. The fibrosis is thought to be caused primarily by the silica and the exact role of the iron pigment in the pathogenesis of the lesion is not clear. The earliest lesions occur as small densely fibrous, sub-pleural foci usually in the upper lobes; these grow by coalescence of adjacent foci until a diffuse fibrosis of the whole lobe is produced. Haematite miner's fibrosis is commonly associated with tuberculosis and other chronic lung infections; in addition there is quite a high incidence of carcinoma of the lung reported in these cases. -

Silicosis
A gold miner using a rock drill with a water spray in an attempt to prevent the occupational disease silicosis, caused by dust inhalation. -

Lotus Leaves (Full Leaf)
"Gabriel Orozco's interest in the natural world and its relationship with humans inspired him to have actual lotus leaves etched into the printing plates, creating a man made yet true rendering of the leaf. Every vein, tear, and insect bite was captured and imprinted on special custom milled Gampi paper matching the hues of the leaf. The proofs were made as chine collé soft ground etchings, individually cut to the shape of each leaf. Orozco had a revelation while holding one of the tissue thin leaf prints up to the window: the exquisite purity that he was seeking was best displayed deconstructed and suspended in glass, illuminated all around, like a delicate specimen. The somewhat unorthodox technique used for this edition was an exciting challenge that resulted in a series of lifelike images that honors the natural world "(Lapis Press 2021). -

Tobacco Mosaic Virus
During the late 19th century, tobacco farmers observed a strange occurrence on the leaves of their tobacco plants. A mosaic pattern of light and dark green (or yellow and green, in some instances) appeared on the leaves of their crops, the presence of which signalled the steady decline in the plant’s growth. Because of the lucrative nature of the industry, finding a treatment for this seemingly infectious disease became a priority, with many laboratories working to isolate the cause. Bacteria were recognised as the causative agents of many infectious diseases of plants and animals, including humans, in the second half of the 19th century – and the technique of filtration was developed to separate infectious agents from extracts or exudates in order to study these microbes. It was whilst utilising this technique that Dmitri Ivanovski, a Russian microbiologist working in the Crimea in 1890, made a surprising discovery. Using the Chamberland–filter made from porcelain and designed to trap ordinary bacteria, Ivanovsky discovered that the filtered sap from the diseased plants could continue to transfer the infection to healthy plants – an occurrence he attributed to an agent which must be an exceedingly small parasitic microorganism, invisible even under great magnification. It would take another 45 years before the visualisation of this subcellular entity would be formulated with the help of an electron microscope, but Ivanovksy, along with the Dutch botanist M.W. Beijerinck, who also and independently, isolated these microbes in his laboratory in 1898, are generally credited for the discovery of viruses. The disease which infected the tobacco plants would be aptly called the Tobacco Mosaic Virus, and its identification would signal the initiation of a field of study known as virology. -

What UCT is not telling its first years
On the 19th of January 2015, an article appeared in the Cape Argus titled 'What UCT is not telling its first years' written by Dr Siona O’Connell, a staff member of the Centre for Curating the Archive, and lecturer at the university. In it she wrote about the absence of transformation in the university, evident in its lack of black academic staff, describing the campus as "mired in unarticulated tensions and divisions, many of them pivoting on race” and “guarded by the Rhodes Memorial – a significant imperialist edifice” that continues to shadow it “in many overt and covert ways” "(O’Connell 2015). In the article she pinpoints that even though, as first years, they will most certainly be greeted by the statue of Cecil John Rhodes overlooking the rugby field during their tour of the campus, their chances of being taught by a black professor during the full span of their degree, will be incredibly slim… -

Canary
Sentinel species are used to detect risks to humans by providing advance warning of a danger. The idea of placing warm-blooded animals in a mine to detect carbon monoxide was first proposed by the Scottish physiologist John Scott Haldane in 1913. Canaries (Serinus canaria ) were considered the best sentinel animals for detection of dangerous gases because they were found to be more sensitive than other species evaluated (Pollock 2016:386-387). -

Flight
A chorus of juvenile heartbeats affected by Atrial Septal (ASD) and Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD), Patent Ductus Arteriosus(PDA), and Aortic Valve Stenosis (AVS), transposed to a higher frequency to simulate birdsong -

An Experiment on a Bird in the Air Pump
In Joseph Wright’s 'An Experiment on a Bird in the Air Pump' (1768), he depicts the re-enactment of Boyle’s famous experiment. Contrary to the restricted viewing of this experiment in the confines of Gresham College by the gentleman of the Royal Society, this audience includes a variety of individuals of different ages and gender, exhibiting a mixture of emotions: a young girl worriedly watches the fate of the bird, while another is comforted by her father, seemingly too upset to view the rest of the experiment; a young boy and middle-aged man look on with absorption, while two young lovers only have eyes for each other; lastly an old man meditates on a skull in a jar, and the scientist stare out at the viewer, and not at the experiment. -

Heart of Cape Town Museum
Christiaan Barnard did forty-eight trial transplants with dogs before he undertook such an operation with a human being. -

Bird Mark 7 Respirator
Dr. Bird invented a number of popular medical devices that were used to care for patients with breathing problems. During WWII he served in the Army Air Corps where, in addition to training and transport assignments, he studied aircraft and respiratory and cardiovascular problems at high altitude. Two devices that he produced during the war went into the design of his first commercial ventilator, the Mark 7 Respirator. Dr. Bird’s respirators and anesthesia ventilators have been used during many of the first human surgical procedures. Among these were the first open heart procedure and the first liver transplant. -

Igemfe
"The transverse flute is rarely seen among the Zulu, who, if they make and use it, call it igemfe, the name of a totally different instrument. I possess three specimens, one from Inchanga, one from Pietermaritzburg district, and one from Ixopo. The first two are open at the end opposite the embouchure, and have three finger-holes; the third is a curiously aberrant example, being closed at both ends and having four finger–holes arranged in pairs" (Kirby 2013: 179) Hornbostel-Sachs number: 421.121.32 Stopped side-blown flutes with fingerholes, Length: 291mm (11.4in), Diameter: 36mm (1.2in), Place of production: St. Michael's-on-Sea (KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa). -

Touching both walls at the same time
As a young sculptor working in the 1960s, Horn suffered severe lung damage from working with fiberglass and polyester, and spent long periods convalescing in hospital. Whilst restricted to her hospital bed, Horn devised a series of wearable sculptures or 'body extensions' which she would later make using cloth, wood, bandages, belts, feathers, and found objects. Her masks and extensions contain, constrain, and/or elongate the bodies of their wearers. -
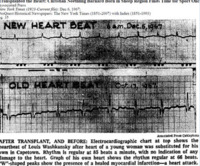
Electrocardiograph of first heart transplant
“The ventricular peaks would shoot up as in wild flight, and their intermediate planes would begin to jumble against one another like the sudden crashing of cars on a freight-train. The heart’s beautiful symmetry would then be reduced to an erratic green line of wild jerks until it entered the final isoelectric phase resembling a sawtooth – jagged lines of the heart seeking to rise like a dying bird, fluttering upward, only to fall once again onto its flat plane of death” (Barnard in Young 2002: 79-80). -
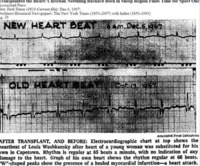
Denise Darvall
"During the first heart transplant a shift occurred in the heart of Denise Darvall, the young brain-dead car accident victim whose family had allowed her heart to be given up. In his account of the operation, Barnard writes how her heart’s life fluid returned from the lungs – how many million times had it happened? – but different this time, void of oxygen. How her heart would react, at first, as if meeting only a small inconvenience. Unaware of what was happening, it would simply pump more excitedly – expecting some relief. Yet this would never come, and it would fall back in the first wave of confusion and fatigue. Barnard equates Darvall's heart with a bird trying to take flight" (Liebenberg 2011: 107-108). -

Touching both walls at the same time
As a young sculptor working in the 1960s, Horn suffered severe lung damage from working with fiberglass and polyester, and spent long periods convalescing in hospital. Whilst restricted to her hospital bed, Horn devised a series of wearable sculptures or 'body extensions' which she would later make using cloth, wood, bandages, belts, feathers, and found objects. Her masks and extensions contain, constrain, and/or elongate the bodies of their wearers. -

Compound of Tincture of Chloroform and Morphine
"Directions: For an adult, from five to ten minims may be taken in a wineglasful of water, and repeated in three to four hours, if necessary. In severe cases, the dose may be increased to fifteen minims. As this preparation contains potent posions, it should be used with caution". (As read on the lable of the bottle) "Action and Uses: In addition to its well-known use as an anaesthetic, Chloroform has been highly recommended for the relief of asthma, and in the form of vaporoles can be employed safely during the passage of calculi from the gall-bladder or kidney. The vaporoles are the most useful in obstetric practice. A vaporole may be crushed and the vapour inhaled from the palm of the hand" (BWC 1896: 38). "Morphine Sulphate: Anodyne. Use with caution. One swallowed gives great relief of pain"(BWC 1925:132).


