Items
Site
The Medicine Chest
Is Part Of is exactly
History
-

Chest: a botanical ecology
Illness and disease affect us all. The treatment of these conditions however, has been vast and varied, depending on the historical periods and the cultural context in and during which they are practiced. Situated in the rock art gallery, where healing power is expressed in San paintings, this mobile set of cabinets explores a rich complex of healing practices through the display of a medicine chest which was donated to the university of Cape Town in 1978. This chest belonged to a British dentist, who practiced in Cape Town from 1904, and who bought the chest for a hunting trip he undertook in 1913 to (then) Northern Rhodesia. The idea of the chest then gives rise to a variety of forms of healing: from instruments used to exorcise evil spirits and children's letters written to celebrate a heart transplant; to medicinal flowers bought at the Adderley Street flower market. The exhibition aims to visualise and materialise illness and its treatment from historical, cultural and disciplinary perspectives. Drawing on well-established historical and contemporary connections between the disciplines of Botany, Medicine and Pharmacology, the exhibits also suggest latent links which are at times political, at times whimsical. -

'Do you think women could be heartsurgens?'
Dear Dr Barnard, I am ten years old. How old are you? I like your heart transplants. When is going to be the next heart transplant? I am a girl. I have two sisters and three brothers. Its too bad I can't see you in person. I live at 2326 Charles St. now. I am moving in 1 day. I will live at 3610 Denny Lane, Franksville, Wisconsin. My name is Sheri Lee Fors. If you have time please write back. Will you please send me your address. Love, Sheri Fors. P.S. Do you think women could be heartsurgens? -

Foxgloves
Called variously foxgloves, witch’s gloves, dead men’s bells, fairy’s gloves, bloody fingers, gloves of our lady, fairy caps, virgin’s gloves or fairy thimbles, Digitalis purpurea is popular with children, who pluck the tempting bell-shaped blooms and wear them like thimbles, admonished not to lick their fingers afterwards for fear they will go blind (Young 2002: 57). While the flower can be lethal if ingested, the drug digitalis derived from foxglove is most commonly used as a heart stimulant. Digitalis has been prescribed since the 17th century, perhaps earlier, as a diuretic and to slow the pulse and is still the drug of choice for atrial fibrillation. In the 1770s, William Withering got an old family recipe, a herbal infusion for treating swollen legs, from a Shropshire woman and identified digitalis as the active one of the twenty ingredients. Many more antiarrhythmic drugs now exist (Young 2002: 57). Made up of surgical gloves, Band-Aids, syringes and IV-tubing (with an infusion of foxglove leaves in its stem) the work mimicked the language of the herbarium specimen, drawing a viewer in to examine the content they were expecting, only to surprise them with its incongruous materials. -

Eucalyptus
"The plants [dislayed in this cabinet] were bought from the Adderley Street flower market in central Cape Town and are used by the sellers for medicinal purposes to treat chest and respiratory problems, with the leaves of the eucalyptus added to a bath and those of the protea infused in hot water and drunk as a broth. The flower sellers trading in Trafalgar Place and along Adderley Street have been doing so since at least the mid-1880s but became viewed as threats to the local flora by the European settlers at about the same time the medicine chest was first introduced to the city at the beginning of the 20th century. The settlers initially preferred to cultivate plants imported from their home countries to indigenous varieties, introducing many species to South Africa for nostalgic or practical reasons (subsequently problematic for local biodiversity) (Van Sittert 2002: 103). In the wake of emerging white nationalism in the 1890s, interest in indigenous plants gained momentum and was deployed to create a sense of belonging to the ‘foreign’ land (Boehi 2013: 133). A botanical discourse was mobilised to underscore ideas about identity and belonging, such as ‘roots’ and ‘ideas of rootedness’, and laws regulating flower picking (which usually occurred on the mountain) were passed in this period and were secured by the Wild Flower Protections Act in 1905 and an amendment thereto in 1908 (Boehi 2013: 133)"(Liebenberg 2021: 275). -

Proteas
"The plants [dislayed in this cabinet] were bought from the Adderley Street flower market in central Cape Town and are used by the sellers for medicinal purposes to treat chest and respiratory problems, with the leaves of the eucalyptus added to a bath and those of the protea infused in hot water and drunk as a broth. The flower sellers trading in Trafalgar Place and along Adderley Street have been doing so since at least the mid-1880s but became viewed as threats to the local flora by the European settlers at about the same time the medicine chest was first introduced to the city at the beginning of the 20th century. The settlers initially preferred to cultivate plants imported from their home countries to indigenous varieties, introducing many species to South Africa for nostalgic or practical reasons (subsequently problematic for local biodiversity) (Van Sittert 2002: 103). In the wake of emerging white nationalism in the 1890s, interest in indigenous plants gained momentum and was deployed to create a sense of belonging to the ‘foreign’ land (Boehi 2013: 133). A botanical discourse was mobilised to underscore ideas about identity and belonging, such as ‘roots’ and ‘ideas of rootedness’, and laws regulating flower picking (which usually occurred on the mountain) were passed in this period and were secured by the Wild Flower Protections Act in 1905 and an amendment thereto in 1908 (Boehi 2013: 133)" (Liebenberg 2021: 275). -

Livingstone
A small wooden chip from the same object collection as the medicine chest balanced on top of one of the bottles from the chest. "The treatment, the Livingstone rouser, was formulated by Dr Livingstone, who, after an attack of malaria in 1853, patented this mixture of quinine and purgatives (calomel, rhubarb and jalop) mixed with opium (Barrett & Giordani 2017: 1655–1666). The chip balanced on its lid is said to be from the almond tree under which he proposed to Mary Moffat in 1844. The juxtaposition of these two objects, one representing the quantifiable and the other the poetic, draws the viewer to consider the conflation of these two realms" (Liebenberg 2021: 273). -

Where the Wild Things Are (Field study)
'Where the Wild Things Are' (21 October – 5 November 2014) explored the political, social and historical narratives embedded in the natural world through investigation, observation, mapping, archival research and art making. The exhibition consisted of various on-site interventions engaging with contemporary and historical spatial dynamics and the significance of Hiddingh Campus. The Egyptian Building (home to sculpture workshops and studios) was built on the site of a zoo established in the late eighteenth century that was replete with lion’s dens and a small lake that supposedly housed a hippo. The campus was also the home to UCT’s first Zoology and Botany building (now the Michaelis Building). This historical perspective highlights both the site’s colonial imprints and its early affiliation with the sciences. The UCT campus is divided into its main upper campus, a middle and lower campus, and a few satellite campuses, of which the Michaelis School of Fine Art and the South African College of Music form part. Students drew on the methodologies of artist/curator Mark Dion, collaborating with specialists from upper campus (entomologists, ornithologists and botanists) and Michaelis Fine Art students, to highlight its natural environment. The interventions occurred on different days, and over a two week period. A calendar was provided to stipulate event times and artwork appearances. Curated by Nina Liebenberg Participating artists: Christopher Swift, Dillon Marsh, Fritha Langerman, Thuli Gamedze, Pippa Skotnes, Alex Kaczmarek, Rone-Mari Botha, Jessica Holdengarde, Fanie Buys, Lara Reusch, Stephani Muller, Tegan Green, Evan Wigdorowitz, Mariam Moosa, C J Chandler, Adrienne Van Eeden-Wharton -

A 'Jungle'
"A ‘jungle’ consisted of a selection of pathological specimens from the Pathology Learning Centre that had been affected by typhoid fever, ascaris adult worms, yellow fever, amoebic ulcerations, tuberculosis and malaria. The diseases that afflicted these specimens were regarded as ‘tropical’. As described in Chapter One, BWC used the jungle as a significant terrain that called for a medicine chest to combat pathogens: ‘Whether you were valiantly saving your compatriot in war, traversing a dark African jungle, navigating one of the world’s first flying machines, exploring the most desolate place on earth, ascending the highest mountain in the world, or simply enjoying the windswept British coast, the chest would be there, ready for any ailment’ (Johnson 2008b: 255). BWC promoted their chests as the ideal antidote for a tropical landscape ‘at once full of potential wealth for imperial Britain, but simultaneously rife with disease’ (Johnson 2008b: 258) and claimed that the tropical colonies were ‘by far the most dangerous regions for travellers’ (BWC 1934: 8). It was here that ‘desolating ailments’ were encountered, all ‘particularly fatal to the so-called white man who originates in temperate climates’ (BWC 1934: 8). I adapted the colour of the images of afflicted intestines, livers, stomachs and brains and used them as material to construct a dense jungle that referenced this aspect of the medicine chest’s history. Printed on separate glass sections that fit into the cabinet at spaced intervals to create an illusion of depth and three-dimensionality, the work draws on the cross-sectional display technique used in many anatomy museums worldwide, in projects such as the Visible Human Project (1995) and that the artist Damien Hirst references in his works . Creating a visual link between the UCT specimens and the history of these diseases surfaces the occluded racial undertones of these understandings" (Liebenberg 2021: 267). -

Buttons
A display of a collection of pins, buckles and buttons excavated from the washing pools used by slaves on Table Mountain. Taken from their dusty boxes in storage they are currently exhibited as part of Skotnes's 'Division of the World' (Department of Archaeology). -

Isigubu through Gqom
"In 2018, the Zulu drum alleged to have been played during the 1906 Bambatha rebellion against British rule and unfair taxation in the colony of Natal (discussed by Nixon) became the focus of Amogelang Maledu’s Honours research project. In ‘Isigubu through gqom: The sound of defiance and Black joy’, Maledu (who has an undergraduate degree in Anthropology and Visual Culture) used the drum’s history of colonial resistance and contextualised it through the contemporary musical genre of gqom, showing music as both an act and celebration of joy and freedom and of defiance against the limitations of township life. Through her ‘speculative and imagined interconnectedness’ of the isigubu and gqom, Maledu appropriated the limited information available about the former and expanded it by reinventing new historical pathways that reframed colonial narrations and aesthetics (Maledu 2018: 29–30). Her curation broke the silence of the Kirby instruments and liberated the isigubu from its ethnomusicological framework through a juxtaposition that spoke back to history and the contemporary moment. In addition, a website provides a framework for historicising gqom and encouraged the growth of its archive through viewer engagement, also highlighting the speculative and stagnant colonial archive in which the isigubu is situated (Maledu 2018: 29–30)" (Liebenberg 2021: 211 - 212). -
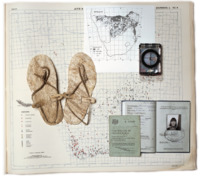
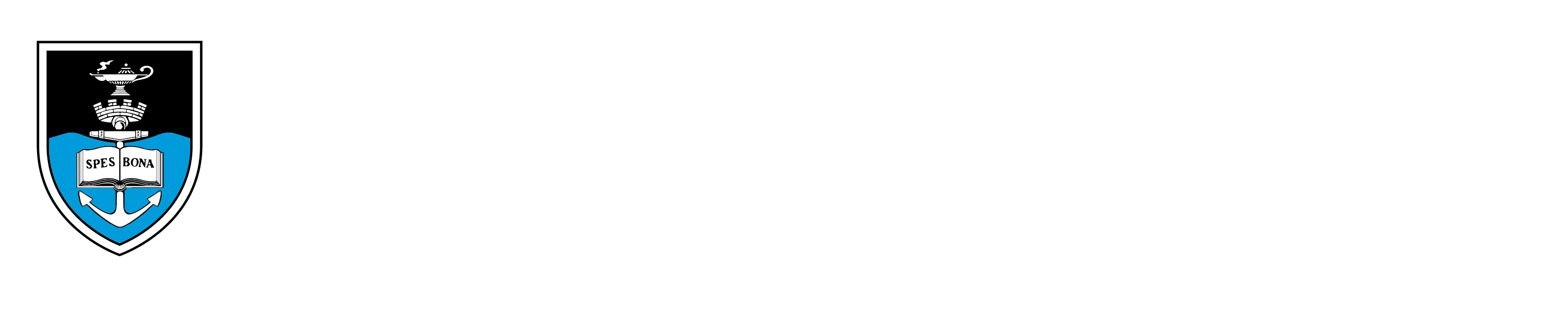
Page 175 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue
"The page presents a curated collection of images: a map from the Avian Demography Unit illustrating the distribution of the bataleur Terathopius ecaudatus along the political border, though the bateleur is more frequently found where there is no formal farming; a Ngwato child’s oxhide sandals collected by Isaac Schapera (a British social anthropologist who worked in South Africa and Botswana); a compass; the identification documents of Paula Ensor (previous dean and Professor of Education), who spent time in exile in Botswana; and a Certificate of Registration necessary for movement across borders, all of which are overlaid on top of a large map from the Afrikaans Atlas provided by Rajend Mesthrie of the Department of Linguistics and Southern African Languages that shows the Afrikaans language’s distribution. Contextualising all of these objects in relation to the large map cuts across disciplinary boundaries and illustrates the scope and impact of the colonial and apartheid regimes and their influence on immigration laws, language studies, ornithology and anthropology" (Liebenberg 2021: 193). -

Pages 38-39 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue
"Objects and collections can reflect naturalisations that occur when the disciplinary perspective renders its subject matter in terms of what it deems worth looking at and how it should be looked at (Daston & Galison 2007: 23). This process has dual consequences, resulting in the honing of a specialised insider focus directed at the object and a blindness to qualities that sit outside the disciplinary frame of reference (as discussed in relation to the Drennan and Kirby collections). 'Curiosity CLXXV' drew on and challenged both these aspects by forcing objects into visual conversations outside their discipline and inviting insiders to view them in these new configurations. These curatorial strategies enabled insiders to become aware of characteristics not normally deemed important in their discipline and to identify the characteristics their discipline did deem important (their attentional subculture, in other words) in objects not studied in their field" (Liebenberg 2021: 180). -

Etching from 'Sound from the Thinking Strings'
"Skotnes’s own visual interpretation of the history and cosmology of the |xam formed the last component of this interdisciplinary endeavour and constituted a visual component that drew together the various strands of disciplinary interpretations and presented a perspective on the |xam life she felt ‘was missing from the other interpretations’ (Skotnes 1991: 30). In these images she drew freely on San mythology, accounts of |xam life recorded by Lucy Lloyd, historical and archaeological research and images from rock paintings in a landscape setting. She writes in her preface that these etchings were direct attempts at ‘inverting the museum dioramas’ in the ethnographic halls close to the exhibition and which, through their display of the San’s body casts, rendered them closer to specimens of biology than as members of a highly developed culture (Skotnes 1991: 52). By creating images that combined shamanistic rituals, entoptic spirals, plants, hunting bags, bows and arrows, snakes, eland-shaped rainclouds, colonists, musical instruments, shelters and therianthropic shapes, Skotnes eclipsed the static narratives of the dioramas and the object labels in the exhibition, placing them in a context in which their metaphysical qualities were celebrated more than their physical qualities. These prints stood in striking contrast to the other exhibits, which framed the San as physical types, and they challenged viewers to confront the reality that the San had a rich history and cultural and social life" (Liebenberg 2021: 157). -

Sound from the Thinking Strings (installation detail)
"Skotnes had a longstanding relationship with the museum, which started when she was still a student at the Michaelis School of Fine Art. Davison remembers that Skotnes would visit the taxidermy section of the South African museum to draw bones. As an anthropologist, Davison admits to finding Skotnes’s way of looking at things stimulating – an individual way of looking at objects that made her look at them differently, even though she was already very familiar with these materials. Davison recalls a visit to the ethnographic stores during which she showed Skotnes the San skin bags, carefully conserved in their drawers and laid out on acid-free paper. Skotnes admired not only their aesthetic qualities but related the stories she had been studying in the Bleek and Lloyd archive to them – stories that shifted their status from anthropological museum objects to powerful animate objects in San spiritual and social life (P. Davison, personal communication, 28 January 2021). Skotnes remembers that she asked staff whether they knew what was inside the bags and was shocked when nobody could remember looking in them. She was allowed to look inside one and found a claw, which they thought must be a leopard’s (P. Skotnes, personal communication, 9 May 2021)" (Liebenberg 2021: 2015). -

Miscast (installation detail)
Instruments from the Kirby collection displayed as part of the 'Miscast' exhibition. -

The Kirby collection of musical instruments
"Kirby’s choice of an ‘age-old simple classification’ to order the instruments can be correlated with another classification formulated at Wits around the time he was collecting. The Department of Bantu Studies was established in the 1920s at roughly the same time as the Music Department. Kirby’s use of the phrase ‘native races’, which features in the title of his book, resonates with the descriptive subtitle of the Wits journal connected to research in this department: Bantu Studies: A Journal Devoted to the Scientific Study of Bantu, Hottentot, and Bushman (Nixon 2013: xii). The homogenising act of categorising all diverse indigenous South African groups into three general categories seems to echo Kirby’s taxonomic imposition on the diverse instruments he collected on his trips and that continues to feature as the ordering principle of this collection" (Liebenberg 2021: 136). -

The workshop
"Held in the Department of Human Biology in the Division of Clinical Anatomy and Biological Anthropology, this collection consists of prepared specimens – both bottled and plastinated, anatomical models – and a skeletal repository used for research purposes. The materials are kept in three separate rooms, with the anatomical models in one, the prepared and plastinated specimens in another and the skeleton repository in its own room behind locked doors, viewable by appointment only. The room housing the anatomical models functioned as a workshop when modelmaking was still offered to first year medical students as an elective course: its walls are lined with shelves that display models made from materials ranging from papier-mâché to modern silicon copies and are taxonomised according to their anatomical representations, such as ‘the eye’, ‘head & neck’, ‘dentistry’, ‘embryology’, ‘lungs’ and ‘cardiovascular system’, to name a few. The models represent each anatomical section and are brightly coloured to differentiate the different parts of the human body and aid in identification. Many of the models can be dismantled into separate pieces and, like a puzzle, be reassembled into their original shapes. Interspersed with these models are rolled-up charts depicting organs, bodily systems and anatomical sections of the body in two-dimensional form, as well as old student modelling projects. A selection of animal skeletons is displayed on the far side of the room, and a shelf with a few anatomical specimens in formaldehyde is across from it" (Liebenberg 2021: 121 - 122). -

'Villus of the small intestine wall'
A student model of the ‘Villus of the small intestine wall’ found in the workshop of the Anatomy Building, UCT. -

Page 65 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue
Page 65 of the 'Curiosity CLXXV' catalogue, showing the Old Anatomy Lecture Theatre (currently part of the Centre for Curating the Archive). -

Page 79 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue.
"Created by Felix von Luschan, an Austrian doctor, anthropologist, explorer, archaeologist and ethnographer in the early 20th century, the chart, known as the Von Luschan chromatic scale (...) was used to classify skin colour and featured as a tool in race studies and anthropometry of the time. Forgotten by its current department staff and students, its presence draws attention to the role of medicine and science in the apartheid agenda and to the larger racist scientific practices of measuring and classifying human physical differences in the 19th and 20th centuries to produce a ‘typology of race’ (Sturken & Cartwright 2018: 351–352). To support such theories, object collections in scientific university departments worldwide also featured collections of human remains; tools for measuring the size and shape of skulls; and charts detailing various physiognomic features (Sturken & Cartwright 2018: 351 – 352)" (Liebenberg 2021: 122 - 125). -

Diary of an oologist
"In 2019, Honours in Curatorship student Nathalie Viruly, who completed her Bachelor of Social Science in Politics and Sociology, was similarly struck by the silence and loss evoked by the [Peter Steyn] collection. Viruly honed in on the moments documented in the notebooks, which capture the loss of life in the reproductive life of these birds and reveal ‘stories of avian tragedy’: Young taken by predator; 1 young accidentally killed; 2 eggs failed to hatch; 2 infertile; Chick disappeared without a trace; Eggs disappeared; Literally cooked by the [corrugated] roof; Nest empty – egg collectors? (Viruly 2018: online). Her focus on these moments in the scientific journal poignantly reveals the conflation between science and emotion and invites the viewer to re-examine hierarchies of loss" (Liebenberg 2021: 219). -

Stone tools
"By positioning artefacts to emphasise their labelling (stones are positioned to reveal the details written on them), including seemingly familiar objects and expanding and shrinking timelines, the installation [Division of the World] draws attention to the framing devices, tools and methods of the department’s insiders" (Liebenberg 2021: 207). -

Things archaeological insiders look at
A variety of pottery shards of Asian porcelain, European earthenware and British stoneware in a drawer in the Department of Archaeology, UCT. -

‘Mrs Glover attending to an ill African chief.’
"The figure of ‘Mrs Glover’, kneeling and treating what appears to be a very ill man, exudes not only the authority of Western medicine within the local context but conveys her as the self-sacrificing and caring European ‘civilizer’ in service of expanding the empire, ‘the medicine chest conveniently by her side’ (Johnson 2008b: 259)" (Liebenberg 2021: 63 - 65). -

Hoard
"The chest was featured in a work titled 'Hoard', for which Bloch sculpted in clay the objects in the UCT collection as well as ones from the 11th century Mapungubwe collection (housed at the University of Pretoria). She painted these sculpted objects gold and presented them in museum display cases, drawing attention to the arbitrary nature of objects’ value and to the possibility that historically loaded items can be accidentally overlooked and misevaluated (Bloch in Honigman 2014: online)" (Liebenberg 2021: 82 - 84). -

Fools and other stories
My copy of Ndebele’s 'Fools and other stories', read and underlined in 2001. -

Page 81 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue.
"At the opening of the Archive and Archive and Public Culture programme (APC) in 2009, Prof. Ndebele stated that ‘there can be no transformation of the curriculum, or indeed of knowledge itself, without an interrogation of archive’, a call which both the Centre for Curating the Archive and the APC have sought to answer by producing scholarship that questions and expands what we understand as ‘archive’ and its relevance in a South African context and in an African university (Skotnes 2019: 21)" (Liebenberg 2021: 195). -

A teeth mould guide
"The large quantity of papers in the BC666 collection pertaining to dental matters – which includes ‘legal and financial papers of the dental practice, papers of the various dental societies to which Walter belonged from 1905 to 1934’ and letters on various dental matters, as well as a large section devoted to correspondence, memoranda and notes on the Medical, Dental and Pharmacy Act of 1928 – shows he was ‘very active in dental politics’ (Hart & Lydall 1981: 1). As an 'office-bearing member of the Dental Society of the Cape Province, and a member of the South African Dental Association, he was the key figure in formulating and presenting the dentists’ case against unqualified dental mechanics in the proposed new medical bill, which was passed in 1928 as the Medical, Dental and Pharmacy Act' (Hart & Lydall 1981: 1). This act was considered a milestone in the development of organised medical, dental and pharmaceutical practices in South Africa, establishing a single set of regulations for these professions across the country (Ryan 1986: 149–151). It was also, however, one of a series of laws passed in South Africa that have regulated indigenous medical practices since the 19th century. Legislation passed in 1862 prevented sangomas from practicing (Paarl in Bishop 2010: 14), and the 1928 act barred inyangas from practicing in all parts of the country except Natal, where they could continue to practice if granted a license (Flint in Bishop 2010: 14–15). The act also banned the indigenous use of ‘European’ methods of diagnosis and treatment, for example forbidding the use of stethoscopes by inyangas (Bishop 2010: 16)" (Liebenberg 2021: 53 - 55). -

Seeing
Educational models found in the Anatomy workshop: "Borrowing from Herbert Read’s art historical discussion on looking, Digby posits that the biomedical practitioner’s generally critical attitudes were shaped in part by their limited recognition of indigenous medicine during this period – ‘what we see is inseparable from how we see; the eye is not innocent, and vision is partial’ (Digby 2006: 356) and, quoting Read, ‘we see what we learn to see, and vision becomes a habit, a convention, a partial selection of all there is to see’ (in Digby 2006: 356). Accordingly, Digby argues that the Western practitioners would have had, at best, only a partial view of the different medical systems in South Africa during this period (Digby 2006: 357) and probably only to the extent that it was a threat to their own livelihood and authority – as evidenced in the 1928 Medical, Dental and Pharmacy Act that Floyd helped instate" (Liebenberg 2021: 55). -

Rattles in the Kirby collection
A drawer of rattles in the South African College of Music's Kirby collection: "The instruments are now grouped in different cabinets according to the taxonomy set out by Kirby in his book. In the preface to the second edition (1964), Kirby shares some of his considerations when deciding how to group the instruments, writing that he had to decide ‘whether to arrange his material tribally, or to deal with each type of musical instrument separately from the technological and historical points of view, allowing the tribal aspects to emerge incidentally’ (Kirby 1964: xi). Kirby chose the second alternative, stating that his chief reason was that he wanted the work to be, as far as possible, ‘a complete and comparative study of one particular aspect of the life of our aborigines’ (1964: xi). His second consideration was to find the most suitable manner for classifying the instruments, for which he defaulted to the ‘age-old simple classification of musical instruments into three main groups of percussion, wind and strings’ (1964: xi) – a Western system for the classification of instruments and the principles on which they were based. The chapters in his book and the displays in the room are thus grouped into three categories: percussion – ‘rattles and clappers’, ‘drums’, ‘xylophones and sansas’ and ‘bull-roarers and spinning-disks’; wind instruments – ‘horns and trumpets’, ‘whistles, flutes, and vibrating reeds’ and ‘reed flute ensembles’; and stringed instruments – ‘stringed instruments’ and ‘Bushmen and Hottentot violins and the ramkie’. Kirby encountered one taxonomic anomaly when employing this system: the ‘gora’, an instrument both wind and string, which he termed ‘a stringed-wind instrument’" (Liebenberg 2021: 135). -

BWC Cape Town premises
"When Burroughs died of pneumonia in 1895, Wellcome became BWC’s sole owner, and the next 20 years (until the outbreak of World War I) constituted a period of massive expansion for the company (Bailey 2008: online). In 1898, the first overseas branch opened in Sydney and was followed by seven more branches – in New York, Montreal, Buenos Aires, Cape Town, Milan, Shanghai and Bombay – by 1912. The Cape Town branch opened in 1902, seven years after Wellcome made his first visit to the city in 1895" (Liebenberg 2021: 49 - 51). -

BWC Cape Town premises (drawing)
Line drawing of the Burroughs Wellcome & Co. office, Cape Town, South Africa. -

Tabloid medicine chest from Scott Polar Expedition
The expedition carried with them a Tabloid Medicine Chest. On the 11th of March, knowing that the party was unlikely to survive, Scott ordered Edward Wilson, the expedition’s Chief Scientist and a qualified doctor, to divide the painkillers between them so they could each end their life on their own terms. Writing in his diary on that day, Scott states, “I practically ordered Wilson to hand over the means of ending our troubles to us, so that anyone of us may know how to do so". Scott, Bowers and Oates had thirty opium tabloids apiece and Wilson, the morphine. Scotts diary entry on either the 22nd or 23rd of March showed that they had a change of heart however: “no fuel and only one or two left of food — must be near the end. Have decided that it shall be natural — we shall march for the depot with or without our effects and die in our tracks". -

The Landis Museum
A drawing by the artist-curator James Hutchinson (Chapter Thirteen) based on an audio description of the object as art of the Glasgow International Arts festival. "Nina Liebenberg also undertakes a form of object analysis at an institutional border. She spent an afternoon in the strongroom of the University of Cape Town's special collections department, examining an early 20th century medicine box commissioned for a hunting trip in (then) Northern Rhodesia. Such boxes had been essential parts of the British colonial project, and allowed emigres, missionaries and explorers to venture deeper into unknown territory without fear of contracting tropical diseases. Liebenberg’s report from the strongroom acts as a set of instructions for The Landis Museum’s curator to make a drawing of the box, to which he has no physical access". Extract from the 'Exhibition Guide' of the Landis Museum (Chapter Thirteen), Glasgow International Arts Festival, 20 April - 07 May 2018. -

Rice child (Stirrings)
"An object-study of a grain of rice by the artist Elaine Gan similarly shows the intermingling temporalities of humans, nonhumans and machines through an assemblage of images, text and vectors maps. Gan explores four temporalities within this research – the time of technologies, matter, memory and a calendar year – and installs the work as a long horizontal strip that cannot be viewed in full from a fixed position but encourages the viewer to walk ‘through time, occupy multiple positions’ and in so doing ‘trace new connections’ (Gan 2021). Time-travelling over two thousand years, Rice child (Stirrings) (2011) begins in the Mekong Delta, where the farming of champa rice facilitated the formation of stable settlements. It then follows a selection of rice varieties, revealing how they became technologies that accumulate socio-political formations, and weaves through the 2007/8 food crisis" (Liebenberg 2021: 28). -

Silver Particle / Bronze (After Henry Moore).
"In Simon Starling’s work, inanimate objects are activated in various ways, especially when their political or economic history is revealed or when their materiality becomes an embodiment of something discovered during his research. His work enables and celebrates diverse interpretations of objects in many instances, as Greenblatt (1991) notes when referring to artistic and curatorial activity, deflecting attention away from the object onto the systems that gave rise to it in the first place. Starling conducts a close inspection of his objects, usually following a web of connections across the globe and across history, which in many of his works lead him back to the starting point; a vintage photograph of a Henry Moore sculpture leads to the production of a bronze sculpture based on the shape of a single enlarged silver particle that makes up the photograph and which, when converted into a sculpture, resembles the biomorphic shapes that served as inspiration for the Moore sculpture in the original vintage photograph ('Silver particle/bronze (after Henry Moore)', 2008). The machinations of its history somehow lost in the image when seen in the museum archive come back into play through the translations and reconstructions encountered in the detour and are materialised in the exhibition format" (Liebenberg 2021: 26 - 28). -

'How Zoology was taught in the past'
The wall text accompanying these charts in the Hunterian museum, Glasgow, reads: "In the late 19th and 20th centuries, before the advent of colour slides that could be projected, the teaching of Zoology depended heavily on the use of wall charts to illustrate lectures. They were hung on a special pulley system at the front of the lecture theatre and, because of their large size, could be clearly seen from the back of the class". -
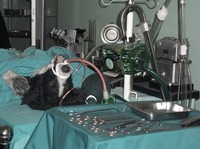
Dogs in the Heart of Cape Town
The guided tour of the museum, which commemorates the first heart transplant performed by Chris Barnard in 1967, starts with a representation of the car accident that provided the heart for the transplant, through to the animal lab where Barnard conducted experiments with over 50 dogs to perfect the technique of heart transplantation. From there one can tour a model of Denise Darvall's bedroom and Christiaan Barnard's office before seeing a recreation of the surgery in the actual operating theaters where it occurred. -

Second star to the right and straight on 'til morning
Cyanotype on paper. Ink on perspex. The work shows the exact positioning of the stars from J.M. Barrie’s window at 3 Adelphi Terrace, London (51°30'N 0°7'21"W), on Saturday, 19 June 1937 – the night of his death. Based on the direction of his window, I was able to locate the ‘second star to the right’ at the 45 degree angle he would have stood and viewed the night sky. Hopefully, he reached his destination, after departing the flat and traveling ‘straight on till morning’. -

Falling stars
Published in 1841, Jackson’s guide was the first of a series of guides published during this period which offered notes for the traveller on appropriate conduct in the field – from providing methods for training the eye to observe what was deemed as relevant details, to instructions on which precision instruments should be carried and how to use them to record and inscribe the results of observations made (Withers 2013: 170). As Jackson states, his guide pointed out to the “uninitiated Traveller what he [sic] should observe, and to remind the one who is well informed, of many objects which (…) might escape him” (Jackson 1841: i). -

Navigation chart, Micronesia
"Early Pacific seafarers did not have scientific instruments or conventional European-style maps to voyage to, and settle, the thousands of islands of Micronesia and Polynesia. Instead they used the movement of the sea, the direction of the wind, the position of the sun and stars, and the flight of birds. This is a navigation chart, obtained by Georg Irmer, the Governor of the Marshall Islands from Chief Nalu of Jaluit atoll in 1896. The strips of wood, bound by cane, represent the currents and winds, and the six small, white shells represent islands". -

The hut
Captain Scott writes in his den in the Terra Nova hut in this October 7, 1911. -

“I am just going outside and may be some time"
After initially making good progress, Terra Nova expedition party’s prospects steadily worsened as they struggled northward. Deteriorating weather, frostbite, snow blindness, hunger and exhaustion led to Edgar Evans dying on 17 February and Lawrence Oates, whose condition was aggravated by an old war-wound to the extent that he was barely able to walk, voluntarily leaving his tent on 16 March and walking to his death. (“I am just going outside and may be some time".)" (Liebenberg 2011: 75). -

Terra Nova
Robert Falcon Scott’s Terra Nova expedition reached the South Pole on 17 January 1912 — 23 days too late. Inside a small tent supported by a single bamboo flying a Norwegian flag, was a record of the five who had been the first to reach the pole: Roald Amundsen, the leader, and his team - Olav Olavson Bjaaland, Hilmer Hanssen, Sverre H. Hassel and Oscar Wisting. On 19 January, they began their 1,300 kilometre journey home, Scott writing: “I’m afraid the return journey is going to be dreadfully tiring and monotonous” (Scott 1914: 548). -

Fish
A showcase of fish found in the Artic regions. -

A label in the Natural History Museum
A label in the Natural History Museum accompanying a discovery made by Mary Anning. -

Your inner fish
"Our hands resemble fossil fins; our heads are organised like those of long extinct jawless fish and major parts of our genomes still look and function like those worms and bacteria" (Shubin 2008). During the summer of his second year of study, paleontologist and evolutionary biologist, Neil Shubin, discovered a particular fossil fish in the Arctic, naming it the Tiktaalik. In Your Inner Fish: A Journey into the 3.5-Billion-Year History of the Human Body (2009) he explored the connections in our human anatomy with those fishes that ventured onto land over 375 million years ago, based on the information gathered from studying the Tiktaalik. -
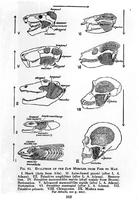
Of fish and men
The evolution of jaw muscles from fish to men. -

Walter Floyd arrives by boat
"The BWC shop was located a short walk from Walter Floyd’s dental practice which he bought in 1904 (for £2,404 16s 8d) and shared with his partner, William Johnston. It is uncertain when Floyd first came out to South Africa, but records prove that he was living here by January 1902 (Hart & Lydall, 1981: 1)" (Liebenberg 2021: 52). In interviews with Mary Floyd in 2015, I showed her this photo of her father-in-law on the boat, en route to Cape Town, and asked her whether she knew who the woman in the photo was. (She appeared in quite a few photos of Floyd's from this period – one especially intimate one showing her lying on a beach and smiling coyly at the photographer.) Was it Agnes, perhaps? She said it definitely wasn't. -

Diving the Tacoma Narrows Bridge
"All that debris still remains under the bridge for the most part, and it has become a dive site. It is a very difficult dive site to get to because of the swiftly moving water and the very short period of slack time. Nature in this area has just a tremendous ability to take over. You have a man-made structure like the Tacoma Narrow Bridge that collapsed into the water. Very quickly, the ocean took it over and made it part of the habitat". Extract from the voiceover of trailer for 700 Feet Down (a documentary about the Tacoma Narrows Bridge told through witnesses of the bridge’s 1940 demise as well as intrepid divers exploring a reef of wreckage, ultimately reflecting on how history influences the present)


