Items
Site
The Medicine Chest
Is Part Of is exactly
Human Biology
-

First Aid: Homage to Joseph Beuys
This work by the artist, Susan Hiller, consists of 13 vintage felt-lined wooden first aid boxes, 86 vintage bottles, water from holy wells and sacred streams, and vintage medical supplies. -

'Do you think women could be heartsurgens?'
Dear Dr Barnard, I am ten years old. How old are you? I like your heart transplants. When is going to be the next heart transplant? I am a girl. I have two sisters and three brothers. Its too bad I can't see you in person. I live at 2326 Charles St. now. I am moving in 1 day. I will live at 3610 Denny Lane, Franksville, Wisconsin. My name is Sheri Lee Fors. If you have time please write back. Will you please send me your address. Love, Sheri Fors. P.S. Do you think women could be heartsurgens? -

Foxgloves
Called variously foxgloves, witch’s gloves, dead men’s bells, fairy’s gloves, bloody fingers, gloves of our lady, fairy caps, virgin’s gloves or fairy thimbles, Digitalis purpurea is popular with children, who pluck the tempting bell-shaped blooms and wear them like thimbles, admonished not to lick their fingers afterwards for fear they will go blind (Young 2002: 57). While the flower can be lethal if ingested, the drug digitalis derived from foxglove is most commonly used as a heart stimulant. Digitalis has been prescribed since the 17th century, perhaps earlier, as a diuretic and to slow the pulse and is still the drug of choice for atrial fibrillation. In the 1770s, William Withering got an old family recipe, a herbal infusion for treating swollen legs, from a Shropshire woman and identified digitalis as the active one of the twenty ingredients. Many more antiarrhythmic drugs now exist (Young 2002: 57). Made up of surgical gloves, Band-Aids, syringes and IV-tubing (with an infusion of foxglove leaves in its stem) the work mimicked the language of the herbarium specimen, drawing a viewer in to examine the content they were expecting, only to surprise them with its incongruous materials. -

The Mother of all Firewalls
'The Mother of all Firewalls' (2012), is a sculptural piece by Kim Gurney made from beeswax, gold glitter, bitumen, repurposed tiles, rabbit skin and glue, which seems to depict an EEG graph in its format but in reality references a graph plotted by Google Insights after Gurney inputted a range of new words that emerged from the ‘Eurogeddon’ of 2012, showing their incidence in news reports pertaining to this financial crisis between 2008 and 2012. -

Suspicious Mind (Performance)
UCT’s Professor Mark Solms, then chairperson of the NPSA and one of the main organisers of the annual international Neuropsychoanalysis conference (2013), highlights Katherine Bull’s contribution to the 'Suspicious Mind' exhibition as one that stood out for him. His interpretation of the ambidextrous portraits she painted of him reveals an insider’s insight of an outsider object and shows how Bull’s artistic process enables theories postulated in his field to manifest in unusual ways: "She painted my double portrait – with her left and right hand simultaneously – over Skype, and she did the same of my beloved (now deceased) colleague Jaak Panksepp on site at the exhibition. I am the grateful owner of both of those double portraits. They hang in my sitting room, so I am reminded daily of the conference and of my departed friend. It is fascinating to see how Bull’s two hemisphere’s processed both me and Jaak each in their different ways. In both of our cases, her left hemisphere painted us with heads that sloped slightly to the right and contained more precise detail; while her right hemisphere painted us more impressionistically, but I think captured our ‘souls’ more accurately" (Liebenberg 2021: 233 - 234) -

Miscast (Lane reflects)
"Where viewers had to walk over a floor of vinyl tiles printed with photocopied newspaper articles and photographs of the San, Lane reflected on another archaeological parallel: ‘just as the texts and images on the floor represent the debris of a particular history, so too do the artefacts strewn across the surface of a site’ (Lane 1996: 7). Yet in trying to define sites and their history, archaeologists feel ‘they can tread on the debris of their own or others’ ancestors with equanimity, colonizing that space for themselves’ (Lane 1996: 7)" (Liebenberg 2021: 172 - 174). -

Miscast (installation detail)
"In juxtaposing instruments that are still being used (such as the scalpel and the camera) with ones that are not (the Von Luschan skin colour chart and the anthropometric measuring rods), Skotnes set up an opportunity for science to reflect on its past and on the activities and objects of its present, enabling a mode of self-reflexivity that is not a standard part of its day-to-day practices. Through curatorship, she exposed disciplinary practitioners to naturalisations and blind spots within their fields and sensitised them to these previously occluded characteristics" (Liebenberg 2021: 172). -

Weighing Smoke
PAUL That’s the man. Well, Raleigh was the person who introduced tobacco in England, and since he was a favourite of the Queen’s – Queen Bess, he used to call her – smoking caught on as a fashion at court. I’m sure Old Bess must have shared a stogie or two with Sir Walter. Once, he made a bet with her that he could measure the weight of smoke. DENNIS You mean, weigh smoke? PAUL Exactly. Weigh smoke. TOMMY You can’t do that. It’s like weighing air. PAUL I admit it’s strange. Almost like weighing someone’s soul. But Sir Walter was a clever guy. First, he took an unsmoked cigar and put it on a balance and weighed it. Then he lit up and smoked the cigar, carefully tapping the ashes into the balance pan. When he was finished, he put the butt into the pan along with the ashes and weighed what was there. Then he subtracted that number from the original weight of the unsmoked cigar. The difference was the weight of the smoke. TOMMY Not bad. That’s the kind of guy we need to take over the Mets. PAUL Oh, he was smart, all right. But not so smart that he didn’t wind up having his head chopped off twenty years later. (Pause) But that’s another story. -

Dialogue goggles
-

A display on page 97 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue
"A stainless-steel dilator from the Drennan collection, a carded set of glass slides of xenopus heart sections from the Medical Microbiology collection, a 19th century game called 'Frogs and Toads' from Special Collections and a wax model of an embryo, also from Drennan. This ‘amphibian’-inspired display showcases many qualities of the curatorial method, such as visual quotation (the combination of these materials foregrounds that the shape of the dilator resembles a frog), analogy (the wax embryo, dilator and frogs allude to the resemblance between sperm and tadpoles) and juxtaposition (the frog as a scientific topic dissected and contained in the slides, and the frog as a board piece in a game played by children)" (Liebenberg 2021: 183). -

A teeth mould guide
"The large quantity of papers in the BC666 collection pertaining to dental matters – which includes ‘legal and financial papers of the dental practice, papers of the various dental societies to which Walter belonged from 1905 to 1934’ and letters on various dental matters, as well as a large section devoted to correspondence, memoranda and notes on the Medical, Dental and Pharmacy Act of 1928 – shows he was ‘very active in dental politics’ (Hart & Lydall 1981: 1). As an 'office-bearing member of the Dental Society of the Cape Province, and a member of the South African Dental Association, he was the key figure in formulating and presenting the dentists’ case against unqualified dental mechanics in the proposed new medical bill, which was passed in 1928 as the Medical, Dental and Pharmacy Act' (Hart & Lydall 1981: 1). This act was considered a milestone in the development of organised medical, dental and pharmaceutical practices in South Africa, establishing a single set of regulations for these professions across the country (Ryan 1986: 149–151). It was also, however, one of a series of laws passed in South Africa that have regulated indigenous medical practices since the 19th century. Legislation passed in 1862 prevented sangomas from practicing (Paarl in Bishop 2010: 14), and the 1928 act barred inyangas from practicing in all parts of the country except Natal, where they could continue to practice if granted a license (Flint in Bishop 2010: 14–15). The act also banned the indigenous use of ‘European’ methods of diagnosis and treatment, for example forbidding the use of stethoscopes by inyangas (Bishop 2010: 16)" (Liebenberg 2021: 53 - 55). -

A1.44.
The contents of Floyd’s two travelling cases for his hunting trip (BC666 A1.44. Special Collections, University of Cape Town). -

BWC Cape Town premises
"When Burroughs died of pneumonia in 1895, Wellcome became BWC’s sole owner, and the next 20 years (until the outbreak of World War I) constituted a period of massive expansion for the company (Bailey 2008: online). In 1898, the first overseas branch opened in Sydney and was followed by seven more branches – in New York, Montreal, Buenos Aires, Cape Town, Milan, Shanghai and Bombay – by 1912. The Cape Town branch opened in 1902, seven years after Wellcome made his first visit to the city in 1895" (Liebenberg 2021: 49 - 51). -

BWC Cape Town premises (drawing)
Line drawing of the Burroughs Wellcome & Co. office, Cape Town, South Africa. -

Tabloid medicine chest from Scott Polar Expedition
The expedition carried with them a Tabloid Medicine Chest. On the 11th of March, knowing that the party was unlikely to survive, Scott ordered Edward Wilson, the expedition’s Chief Scientist and a qualified doctor, to divide the painkillers between them so they could each end their life on their own terms. Writing in his diary on that day, Scott states, “I practically ordered Wilson to hand over the means of ending our troubles to us, so that anyone of us may know how to do so". Scott, Bowers and Oates had thirty opium tabloids apiece and Wilson, the morphine. Scotts diary entry on either the 22nd or 23rd of March showed that they had a change of heart however: “no fuel and only one or two left of food — must be near the end. Have decided that it shall be natural — we shall march for the depot with or without our effects and die in our tracks". -

Corrections
Examples of Wellcome's design changes annotated on tracing paper. 1914–1938. WF/M/I/PR/O01/3, 4, 9, 8. Wellcome Collection. -

Miscast (instruments of measurement)
"Along with the guides that regulated practices and protocols to stabilise and standardise an individual’s response to unfamiliar and disorienting sights (Kennedy 2013: 42), the gender, class and ethnicity of the observer were also of importance , as was the use of ‘ever more sophisticated instruments and calculations designed to minimize the intrusion of subjectivity into the reporting of information’ (Driver 2001: 55). By regulating who was doing the viewing, stipulating what should be viewed and how and supplying tools to measure these observations, scientific institutions promoted an authoritative ‘way of seeing’ in the field that differentiated the scientific view from that of the ordinary traveller (Driver 2001: 49)" (Liebenberg 2021: 109). -

The Heterotopic Hearts
“On two occasions in 1977, when a patient’s left ventricle failed acutely after routine open-heart surgery and when no human donor organ was available, Barnard transplanted an animal heart heterotopically. On the first occasion, a baboon heart was transplanted, but this failed to support the circulation sufficiently, the patient dying some six hours after transplantation. In the second patient, a chimpanzee heart successfully maintained life until irreversible rejection occurred four days later, the recipient’s native heart having failed to recover during this period. Further attempts at xenotransplantation were abandoned and even now, more than 30 years later, xenotransplantation remains an elusive holy grail despite decades of research.” Extract: Brink JG, Hassoulas J. The first human heart transplant and further advances in cardiac transplantation at Groote Schuur Hospital and the University of Cape Town. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2009; 20(1):31-5 -
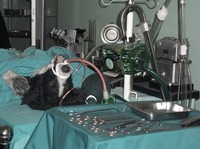
Dogs in the Heart of Cape Town
The guided tour of the museum, which commemorates the first heart transplant performed by Chris Barnard in 1967, starts with a representation of the car accident that provided the heart for the transplant, through to the animal lab where Barnard conducted experiments with over 50 dogs to perfect the technique of heart transplantation. From there one can tour a model of Denise Darvall's bedroom and Christiaan Barnard's office before seeing a recreation of the surgery in the actual operating theaters where it occurred. -

The Brown Dog Affair (1903 - 1910)
On Feb. 2, 1903, English physicians William Bayliss and Ernest Starling, gave a lecture on the digestive system to a theatre full of medical students. Also in attendance were Lizzy Lind af Hageby and Leisa Schartau, committed feminists and anti-vivisectionists. They had travelled from Sweden to enrol at the London School of Medicine for Women, attend lectures around town, and document the practice of vivisection in British universities. During the lecture, a brown terrier was wheeled out, strapped to a board. Starling had already performed one experiment on the dog two months earlier, shutting off its pancreas. This time, Bayliss cut open the dog’s neck and spent half an hour unsuccessfully trying to stimulate the animal’s salivary glands with electrodes. Eventually, he gave up and handed the dog over to a student (Henry Dale, another future Nobel laureate) who stabbed it through the heart, thus ending the lesson. What followed was a court case filed by Stephen Coleridge, a prominent barrister and secretary of the National Anti-Vivisection Society against Bayliss. After four days of testimony, the judge called the women’s account “hysterical” while giving instructions to the jury. The jurors conferred for 20 minutes, then found Coleridge guilty of libel. Anti-vivisectionists commissioned a bronze statue of the dog as a memorial, unveiled in Battersea in 1906. Its plague, which read "Men and women of England, how long shall these Things be?" led to the it being vandalised on a frequent basis. On 10 December 1907, hundreds of medical students marched through central London waving effigies of the brown dog on sticks, clashing with suffragettes, trade unionists and 300 police officers, one of a series of battles known as the ‘Brown Dog’ riots. In March 1910, tired of the controversy, Battersea Council sent four workers accompanied by 120 police officers to remove the statue under cover of darkness, after which it was reportedly melted down by the council's blacksmith. -

A label in the Natural History Museum
A label in the Natural History Museum accompanying a discovery made by Mary Anning. -

Your inner fish
"Our hands resemble fossil fins; our heads are organised like those of long extinct jawless fish and major parts of our genomes still look and function like those worms and bacteria" (Shubin 2008). During the summer of his second year of study, paleontologist and evolutionary biologist, Neil Shubin, discovered a particular fossil fish in the Arctic, naming it the Tiktaalik. In Your Inner Fish: A Journey into the 3.5-Billion-Year History of the Human Body (2009) he explored the connections in our human anatomy with those fishes that ventured onto land over 375 million years ago, based on the information gathered from studying the Tiktaalik. -
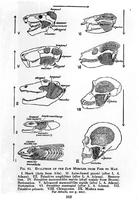
Of fish and men
The evolution of jaw muscles from fish to men. -

A beating heart
"Dear Doctor Barnard I am an 11 year old girl, and I have a problem: I went fishing today; when we came back, my parents cleaned the fish, and after they took out the insides, they found a heart of a fish beating, but the fish was dead and cut up. It was still beating for about 1/2 an hour. Can you explain that? I am very interested in biology, and so is everyone else in my family. Sincerely Yours, Lillian Levy P.S. I know you are a very busy man, but, if you have enough time, please try to answer. THANK YOU! P.P.S. If a doctor says you're dead and they take out your heart but it is still beating, are you dead or alive?" Transcribed letter from the Heart of Cape Town Museum -

Walter Floyd arrives by boat
"The BWC shop was located a short walk from Walter Floyd’s dental practice which he bought in 1904 (for £2,404 16s 8d) and shared with his partner, William Johnston. It is uncertain when Floyd first came out to South Africa, but records prove that he was living here by January 1902 (Hart & Lydall, 1981: 1)" (Liebenberg 2021: 52). In interviews with Mary Floyd in 2015, I showed her this photo of her father-in-law on the boat, en route to Cape Town, and asked her whether she knew who the woman in the photo was. (She appeared in quite a few photos of Floyd's from this period – one especially intimate one showing her lying on a beach and smiling coyly at the photographer.) Was it Agnes, perhaps? She said it definitely wasn't. -

Untitled
An IV drip releases a drop on a handkerchief floating above a fan, drying it before next one falls. -

Sudden death of city dentist
Newspaper article about Walter Floyd's death -

About Ed Ricketts
"Just about dusk one day in April 1948 Ed Ricketts stopped work in the laboratory in Cannery Row. He covered his instruments and put away his papers and filing cards. He rolled down the sleeves of his wool shirt and put on the brown coat which was slightly small for him and frayed at the elbows. He wanted a steak for dinner and he knew just the market in New Monterey where he could get a fine one, well hung and tender. He went out into the street that is officially named Ocean View Avenue and is known as Cannery Row. His old car stood at the gutter, a beat-up sedan. The car was tricky and hard to start. He needed a new one but could not afford it at the expense of other things. Ed tinkered away at the primer until the ancient rusty motor coughed and broke into a bronchial chatter which indicated that it was running. Ed meshed the jagged gears and moved away up the street. He turned up the hill where the road crosses the Southern Pacific Railways track. It was almost dark, or rather that kind of mixed light and dark which makes it very difficult to see. Just before the crossing the road takes a sharp climb. Ed shifted to second gear, the noisiest gear, to get up the hill. The sound of his motor and gears blotted out every other sound. A corrugated iron warehouse was on his left, obscuring any sight of the right of way. The Del Monte Express, the evening train from San Francisco, slipped around from behind the warehouse and crashed into the old car. The cow-catcher buckled in the side of the automobile and pushed and ground and mangled it a hundred yards up the track before the train stopped" (Steinbeck 1951: 279). After Ricketts' death in 1948, Steinbeck dropped the species catalogue from the earlier 'The Sea of Cortez' and republished it with a eulogy to his friend added as an afterword. -

Echolocation (Part one)
In the spring of 1940, Steinbeck and his very close friend, biologist Ed Ricketts, chartered a boat and embarked on a month long marine specimen-collecting expedition in the Gulf of California, which resulted in their collaboration on a book, 'The Sea of Cortez'. Described as both a travelogue and biological record, it reveals the two men's philosophies: it dwells on the place of humans in the environment, the interconnection between single organisms and the larger ecosystem, and the themes of leaving and returning home. A number of ecological concerns, rare in 1940, are voiced, such as an imagined but horrific vision of the long term damage that the Japanese bottom fishing trawlers are doing to the sea bed. Although written as if it were the journal kept by Steinbeck during the voyage, the book is to some extent a work of fiction: the journals are not Steinbeck's, and his wife, who had accompanied him on the trip, is not mentioned (though at one point Steinbeck slips and mentions the matter of food for seven people). Since returning home is a theme throughout the narrative, the inclusion of his wife, a symbol of home, would have dissipated the effect. Steinbeck and Ricketts are never mentioned by name but are amalgamated into the first person "we" who narrate the log. -

Kuhn's Jellyfish
Kuhn's "example illustrates how the entrenched expectations of experimental outcomes and prescribed instrumental functions of an insider’s view of the laboratory and its equipment can pose a threat to new discoveries. The circumstances that enabled Roentgen (an insider) to first notice these new rays are not clear, but Kuhn proposes that the occurrence of anomaly enables discovery and that Roentgen’s ‘recognition that nature has somehow violated the paradigm-induced expectations that govern normal science’ (1970: 52–3) was important. Kuhn emphasises that Roentgen valued the anomaly instead of ignoring it – a vital step in the process of discovery" (Liebenberg 2021: 114). -

Jellyfish
A detail from an X-ray of my jaw -

Eugen Ransonnet-Villez
"Measuring three feet high by two and half wide and deep, this submersible, of sheet iron and inch-thick glass, had the user's legs sticking out of the bottom so that he could propel himself along the seabed at a depth of five meters or so. It was weighed down by cannonballs, and with air pumped in, the diving bell allowed him to descend for sessions of up to three hours" (The Public Domain Review 2021). -

Lithograph of underwater scene
Lithograph of underwater scene by Eugen Ransonnet-Villez, from colour pencil drawings made by the artist while submerged in his diving bell, from his 'Sketches of the Inhabitants, Animal Life and Vegetation in the Lowlands and High Mountains of Ceylon' (1867) -

Melchior & Cousteau
In 1963 Simone Melchior became the world's first female aquanaut by living in Starfish House, an underwater habitat, for the final four days of the Conshelf II project. Although never visible in the 'Undersea World of Jacques Cousteau' series, Cousteau's wife and business partner played a key role in the operation at sea. She was the acting mother, healer, nurse and psychiatrist to the all-male crew for 40 years. Cousteau describes her as being "happiest out of camera range, in the crow’s nest of the Calypso (...), scanning the sea for whales". Her father, Henri Melchior, was director of Air Liquide (France’s main producer of industrial gases at the time) and funded the invention of the aqua lung and the scuba diving apparatus we know today. -

Breath Sculptures
In the exhibition, 'Chest: a botanical ecology', "this cabinet extended the ideas of fragility and fallibility represented by the broken glass laboratory bottle, displaying four ‘breath sculptures’ made by the five individual breaths of children who suffer from asthma: Thaakira Salie (aged 8), Ziyaad Small (aged 10), Blake Leppan (aged 9) and Jessie Allot (aged 11). Working in collaboration with the Allergy Foundation of South Africa and Andre de Jager, UCT’s resident glass blower in the Department of Chemistry, I facilitated a workshop in which the children were taught the practice of blowing glass and then produced their own sculptures by breathing into molten glass. The breath sculptures made by these children were far removed from the functional bespoke glassware usually produced in the workshop for chemical experiments or for those conducted for physics and chemical engineering (A. de Jager, personal communication, 20 August 2018)" (Liebenberg 2021: 263). -

The Northern Lights
Histology slides of the brain (human and animal), scanned and converted into video projection -

Haematite Miner's Lung (Or Sidero-silicosis)
Catalogue No: R3-d55-0331. Origin: UCT Anat Path museum. Old Museum No: V:x:6. Year: not recorded. Clinical data: No further clinical or laboratory details are available other than that the patient was an emaciated 50 year old man. Macroscopy: The specimens preserved are both lungs, the heart, kidneys, spleen and and portions of liver. In the thorax, both pleural cavities were completely obliterated by a fibrous pleurisy of long-standing and both lungs were universally adherent throughout. They were stripped off with difficulty and were found to have thickening of the pleura over the upper lobe on the left side and the upper and middle lobes on the right. The lower lobes on both sides were soft and spongy while the upper lobes were dense and firm on palpation but on section there was no cavitation and no evidence of tuberculosis. The left lung showed a dense fibrosis of the whole of the upper lobe and the upper third of the lower lobe; no crepitant lung tissue could be found in the upper lobe while the lower two-thirds of the lower was crepitant and showed emphysema of a hypertrophic nature. The lung was a dull brick colour and haematite dust flowed out with the fluid when the lung was sectioned. The right lung presented a similar appearance to the left. There was a solid dense fibrosis of the upper and middle lobes and the lower lobe showed fibrosis with hypertrophic emphysema. There was no evidence of tuberculosis and on palpation, a dense fibrosis was found with no nodular formation whatever. On section, it showed a similar appearance of a brick-dust colour, dilated bronchi and uniform fibrosis of the upper and middle lobes with no crepitant lung tissue. The pericardial sac was slightly increased in size due to a hypertrophied and dilated heart. The hypertrophy was mostly on the right side and there was a terminal dilatation of the right atrium; the valves and coronary vessels unremarkable.The liver was small and on section showed venous congestion and cloudy swelling. Microscopy: On microscopy, sections of lung show a diffuse fibrosis of both upper lobes with no recognizable lung tissue. The fibrosis in areas has a slightly whorled arrangement, the centre of which is hyaline and contains no iron pigment and surrounding it is a zone of cellular tissue containing masses of iron. In the upper part of the lower lobe where the lung tissue is recognizable as such, a few nodules definitely resembling silica nodules are to be seen. In the both lower lobes a solid oedema was noted and emphysema marked. The fibrosis was not present to anything like the same extent in the lower lobes, the emphysema being the most marked feature. No evidence of tuberculosis was found in either lung, though a calcareous gland was found in the hilum. Under polarised light, the iron showed up as a golden brown with a few points of light, clear, needle-like in contra-distinction to the iron lying free in the fibrous tissue. The macrophages are beautifully shown lying inside the alveoli filled with iron dust. Percentage of Ash 16.6 Percentage of silica to ash 6.6 Percentage of silica to dry lung 1.1 Percentage of iron to ash 10.3 Percentage of iron to dry lung 6.7 Comments: In summary, the post mortem findings were of: Dense pulmonary fibrosis; hypertrophied and dilated right ventricle; failure of compensation. This condition is described as haematite miner's lung or sidero-silicosis, caused by the inhalation of dust containing silica and ferric oxide which is the principal component of the ore. The fibrosis is thought to be caused primarily by the silica and the exact role of the iron pigment in the pathogenesis of the lesion is not clear. The earliest lesions occur as small densely fibrous, sub-pleural foci usually in the upper lobes; these grow by coalescence of adjacent foci until a diffuse fibrosis of the whole lobe is produced. Haematite miner's fibrosis is commonly associated with tuberculosis and other chronic lung infections; in addition there is quite a high incidence of carcinoma of the lung reported in these cases. -

Pompei casts
-

Silicosis
A gold miner using a rock drill with a water spray in an attempt to prevent the occupational disease silicosis, caused by dust inhalation. -

A1.21-A1.21.1
An object from BC666: Walter Floyd's physiology notes from when he was a student. -

Lotus Leaves (Full Leaf)
"Gabriel Orozco's interest in the natural world and its relationship with humans inspired him to have actual lotus leaves etched into the printing plates, creating a man made yet true rendering of the leaf. Every vein, tear, and insect bite was captured and imprinted on special custom milled Gampi paper matching the hues of the leaf. The proofs were made as chine collé soft ground etchings, individually cut to the shape of each leaf. Orozco had a revelation while holding one of the tissue thin leaf prints up to the window: the exquisite purity that he was seeking was best displayed deconstructed and suspended in glass, illuminated all around, like a delicate specimen. The somewhat unorthodox technique used for this edition was an exciting challenge that resulted in a series of lifelike images that honors the natural world "(Lapis Press 2021). -

Mozart's Antimony
Medical bedside cabinet, gramophone player with a hypodermic needle substitution, Mozart’s Sonata in C, KV 279 and Sonata in D, KV 576. The needle is slowly scratching irreparable grooves into the record whilst the record in return, is making the needle blunt.. "On 20 October 1791, Mozart told his wife Constanza that he was being poisoned. On 20 November he developed a fever; his hands, feet and stomach became swollen, and he had attacks of vomiting. He died on the 5th of December. Although Antonio Salieri confessed to Mozart’s murder several years later, it is highly unlikely as Salieri suffered from senile dementia. In 1991, Ian James of London’s Royal Free Hospital attributed Mozart’s death to antimony, a poison that Mozart may have been given by his doctor - not to kill him but to cure him. Antimony was prescribed for what was then diagnosed as melancholia. In small doses it leads to headaches, fainting and depression. In large doses it can be fatal within days (Emsley 1999: 225). In the autumn of 1791, Mozart, suffering from severe depression, exacerbated by debt, the ill reception of his new work La Clemenza di Tito, and a commission to write a requiem which he believed was for his own funeral, dosed himself with a variety of medicines – one of these being antimony – and what was meant to cure, killed" (Liebenberg 2011: 85 - 91). -

Woman, woman, let go of me
In the chapter he titled, 'When Wendy Grew Up', J.M. Barrie recalls how Wendy tried, for Peter’s sake, not to have growing pains – and how she even felt untrue to him when she got the prize for general knowledge. But the years came and went without bringing the careless boy and Wendy eventually grew up and got married. If you feel sorry for her, don’t. Barrie tells us that Wendy was the kind of girl that liked growing up and that in the end, “ she grew up of her own free will a day quicker than other girls” (1989:182). All grown up with a daughter of her own, Peter visits her again one night while she’s sitting in front of the fire, darning. She hears the crow call and the window blows open as of old, Peter dropping to the floor – looking exactly the same as ever. “He was a little boy, and she was grown up. She huddled by the fire not daring to move, helpless and guilty, a big woman. ‘Hallo, Wendy,’ he said, not noticing any difference, for he was thinking chiefly of himself; and in the dim light her dress might have been the nightgown in which he had seen her first. ‘Hallo, Peter,’ she replied faintly, squeezing herself as small as possible. Something inside her was crying, ‘Woman, woman, let go of me’” (1989: 185 - 186). -

Smallpox
"In Kimberley in 1883-4, several leading doctors with links to the diamond-mining industry publicly denied the presence of smallpox among migrant workers, instead diagnosing them as suffering from a rare skin disease. They appear to have done so lest admitting that the dreaded smallpox was raging, which would have affected the supply of labour and materiel and thereby interrupting mining operations. Led by Cecil Rhodes’s friend, Dr Leander Starr Jameson, measures to curb the epidemic were sporadic or, in the mining compounds, non-existent, and cases topped 2000, with mortality at 3.5 per cent of the population. Only when the colonial government eventually called in external doctors to diagnose the disease, was the cover-up terminated and vaccination, fumigation and isolation vigorously pursued. The conspiracy of denial, by retarding action and sowing doubt about the need to be vaccinated, had been responsible for no small percentage of the 700 deaths in the town" (Phillips 2012: 32-33). -

Canary
Sentinel species are used to detect risks to humans by providing advance warning of a danger. The idea of placing warm-blooded animals in a mine to detect carbon monoxide was first proposed by the Scottish physiologist John Scott Haldane in 1913. Canaries (Serinus canaria ) were considered the best sentinel animals for detection of dangerous gases because they were found to be more sensitive than other species evaluated (Pollock 2016:386-387). -

Flight
A chorus of juvenile heartbeats affected by Atrial Septal (ASD) and Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD), Patent Ductus Arteriosus(PDA), and Aortic Valve Stenosis (AVS), transposed to a higher frequency to simulate birdsong -

An Experiment on a Bird in the Air Pump
In Joseph Wright’s 'An Experiment on a Bird in the Air Pump' (1768), he depicts the re-enactment of Boyle’s famous experiment. Contrary to the restricted viewing of this experiment in the confines of Gresham College by the gentleman of the Royal Society, this audience includes a variety of individuals of different ages and gender, exhibiting a mixture of emotions: a young girl worriedly watches the fate of the bird, while another is comforted by her father, seemingly too upset to view the rest of the experiment; a young boy and middle-aged man look on with absorption, while two young lovers only have eyes for each other; lastly an old man meditates on a skull in a jar, and the scientist stare out at the viewer, and not at the experiment. -

Modest_ Witness@Second _Millenium
Boyle's 'New Experiments Physico-Mechanical Touching the Spring of the Air', which describes experiments with an air-pump, recounts a demonstration attended by high-born women at which small birds were suffocated by the evacuation of the chamber in which the animals were held. Since the ladies interrupted the experiments by demanding that air be let in to rescue a struggling bird, Boyle reported that “to avoid such difficulties, the men later assembled at night to conduct the procedure and attest to the results” (Haraway 2004: 232). -

Heart of Cape Town Museum
"Dear Dr Chris, please tell me how to do a heart transplant". I want to do it to two birds that I have caught. My brother and father own the ELIM Butchery Strand. -

Wings
512 lasercut hands derived from images of healing: 2500 BC - 2000 AD.


