Items
Site
The Medicine Chest
keywords is exactly
Chris Barnard
-

'Do you think women could be heartsurgens?'
Dear Dr Barnard, I am ten years old. How old are you? I like your heart transplants. When is going to be the next heart transplant? I am a girl. I have two sisters and three brothers. Its too bad I can't see you in person. I live at 2326 Charles St. now. I am moving in 1 day. I will live at 3610 Denny Lane, Franksville, Wisconsin. My name is Sheri Lee Fors. If you have time please write back. Will you please send me your address. Love, Sheri Fors. P.S. Do you think women could be heartsurgens? -

Subtle Thresholds (PLC)
"Integrated into the PLC, these works speak to the specimens on display and provide interesting access points to the collection. The animal-faeces prints (which referenced ‘sites of contamination’ in the context of the SAM exhibition) resonate, for instance, with many of the specimens on display in the PLC, such as the heterotopic heart (also called a ‘piggy-back heart transplant’) created by Dr Chris Barnard in 1977, consisting of a baboon heart grafted onto a human heart for additional motoric support. In addition to their more ‘famous’ specimens, the centre also has an extensive intestinal worm collection and many organs affected by zoonotic diseases, such as a liver ravaged by malaria. This was not a conscious decision on the part of the artist-curator and illustrates how curation can draw attention to aspects of a collection and liberate new associations when brought into conversation with it" (Liebenberg 2021: 201). -

The Heterotopic Hearts
“On two occasions in 1977, when a patient’s left ventricle failed acutely after routine open-heart surgery and when no human donor organ was available, Barnard transplanted an animal heart heterotopically. On the first occasion, a baboon heart was transplanted, but this failed to support the circulation sufficiently, the patient dying some six hours after transplantation. In the second patient, a chimpanzee heart successfully maintained life until irreversible rejection occurred four days later, the recipient’s native heart having failed to recover during this period. Further attempts at xenotransplantation were abandoned and even now, more than 30 years later, xenotransplantation remains an elusive holy grail despite decades of research.” Extract: Brink JG, Hassoulas J. The first human heart transplant and further advances in cardiac transplantation at Groote Schuur Hospital and the University of Cape Town. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2009; 20(1):31-5 -
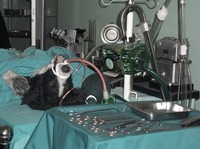
Dogs in the Heart of Cape Town
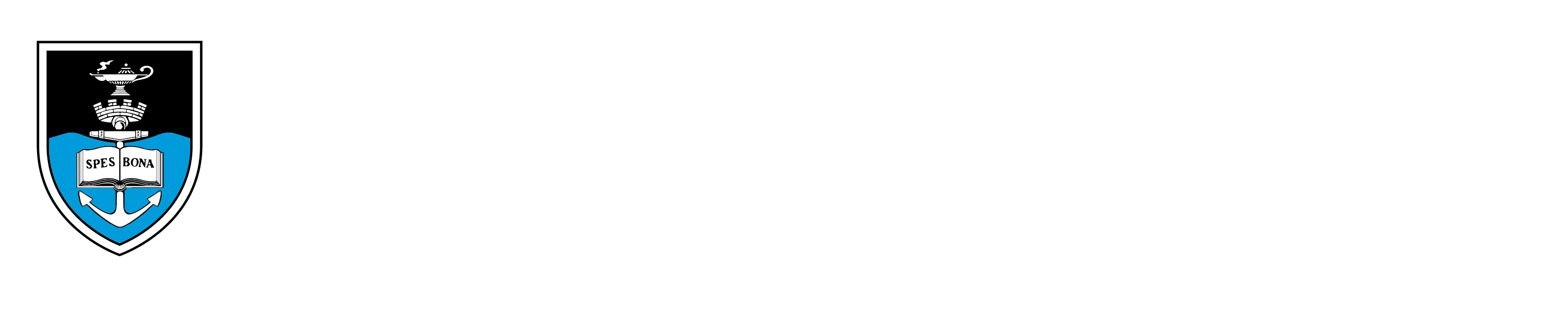
The guided tour of the museum, which commemorates the first heart transplant performed by Chris Barnard in 1967, starts with a representation of the car accident that provided the heart for the transplant, through to the animal lab where Barnard conducted experiments with over 50 dogs to perfect the technique of heart transplantation. From there one can tour a model of Denise Darvall's bedroom and Christiaan Barnard's office before seeing a recreation of the surgery in the actual operating theaters where it occurred. -

A beating heart
"Dear Doctor Barnard I am an 11 year old girl, and I have a problem: I went fishing today; when we came back, my parents cleaned the fish, and after they took out the insides, they found a heart of a fish beating, but the fish was dead and cut up. It was still beating for about 1/2 an hour. Can you explain that? I am very interested in biology, and so is everyone else in my family. Sincerely Yours, Lillian Levy P.S. I know you are a very busy man, but, if you have enough time, please try to answer. THANK YOU! P.P.S. If a doctor says you're dead and they take out your heart but it is still beating, are you dead or alive?" Transcribed letter from the Heart of Cape Town Museum -

Heart of Cape Town Museum
"Dear Dr Chris, please tell me how to do a heart transplant". I want to do it to two birds that I have caught. My brother and father own the ELIM Butchery Strand. -

Heart of Cape Town Museum
Christiaan Barnard did forty-eight trial transplants with dogs before he undertook such an operation with a human being. -

Bird Mark 7 Respirator
Dr. Bird invented a number of popular medical devices that were used to care for patients with breathing problems. During WWII he served in the Army Air Corps where, in addition to training and transport assignments, he studied aircraft and respiratory and cardiovascular problems at high altitude. Two devices that he produced during the war went into the design of his first commercial ventilator, the Mark 7 Respirator. Dr. Bird’s respirators and anesthesia ventilators have been used during many of the first human surgical procedures. Among these were the first open heart procedure and the first liver transplant. -
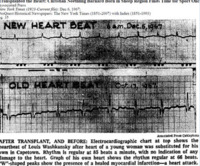
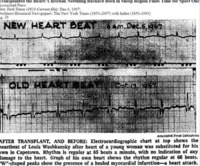
Electrocardiograph of first heart transplant
“The ventricular peaks would shoot up as in wild flight, and their intermediate planes would begin to jumble against one another like the sudden crashing of cars on a freight-train. The heart’s beautiful symmetry would then be reduced to an erratic green line of wild jerks until it entered the final isoelectric phase resembling a sawtooth – jagged lines of the heart seeking to rise like a dying bird, fluttering upward, only to fall once again onto its flat plane of death” (Barnard in Young 2002: 79-80). -
Denise Darvall
"During the first heart transplant a shift occurred in the heart of Denise Darvall, the young brain-dead car accident victim whose family had allowed her heart to be given up. In his account of the operation, Barnard writes how her heart’s life fluid returned from the lungs – how many million times had it happened? – but different this time, void of oxygen. How her heart would react, at first, as if meeting only a small inconvenience. Unaware of what was happening, it would simply pump more excitedly – expecting some relief. Yet this would never come, and it would fall back in the first wave of confusion and fatigue. Barnard equates Darvall's heart with a bird trying to take flight" (Liebenberg 2011: 107-108). -

SP-368 Biomedical Results of Apollo
Electrocardiograph signal received at Mission Control during various periods of the Apollo 11 mission


