Items
Site
The Medicine Chest
keywords is exactly
Covid-19
-

Taxonomy
Visually categorising a selection of my research material (accumulated since 2015). -

Wednesday, 1 April 2020
Marseille, France: A resident of a block of flats is passed food by his neighbours using a rope made of blankets. -

Untitled
An IV drip releases a drop on a handkerchief floating above a fan, drying it before next one falls. -

Wave
Screengrab of an image search, typing in 'third wave' -

Tobacco Mosaic Virus
During the late 19th century, tobacco farmers observed a strange occurrence on the leaves of their tobacco plants. A mosaic pattern of light and dark green (or yellow and green, in some instances) appeared on the leaves of their crops, the presence of which signalled the steady decline in the plant’s growth. Because of the lucrative nature of the industry, finding a treatment for this seemingly infectious disease became a priority, with many laboratories working to isolate the cause. Bacteria were recognised as the causative agents of many infectious diseases of plants and animals, including humans, in the second half of the 19th century – and the technique of filtration was developed to separate infectious agents from extracts or exudates in order to study these microbes. It was whilst utilising this technique that Dmitri Ivanovski, a Russian microbiologist working in the Crimea in 1890, made a surprising discovery. Using the Chamberland–filter made from porcelain and designed to trap ordinary bacteria, Ivanovsky discovered that the filtered sap from the diseased plants could continue to transfer the infection to healthy plants – an occurrence he attributed to an agent which must be an exceedingly small parasitic microorganism, invisible even under great magnification. It would take another 45 years before the visualisation of this subcellular entity would be formulated with the help of an electron microscope, but Ivanovksy, along with the Dutch botanist M.W. Beijerinck, who also and independently, isolated these microbes in his laboratory in 1898, are generally credited for the discovery of viruses. The disease which infected the tobacco plants would be aptly called the Tobacco Mosaic Virus, and its identification would signal the initiation of a field of study known as virology. -
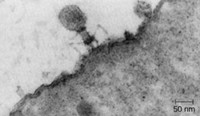
Holes
A virus attacks a cell by attaching itself to the outer wall. It then uses a specialized protein to digest a small hole in the wall of the cell and inject its nucleic acid molecule into the cell's cytoplasm.


