Items
Site
The Medicine Chest
keywords is exactly
Curiosity CLXXV
-

Chest: a botanical ecology
Illness and disease affect us all. The treatment of these conditions however, has been vast and varied, depending on the historical periods and the cultural context in and during which they are practiced. Situated in the rock art gallery, where healing power is expressed in San paintings, this mobile set of cabinets explores a rich complex of healing practices through the display of a medicine chest which was donated to the university of Cape Town in 1978. This chest belonged to a British dentist, who practiced in Cape Town from 1904, and who bought the chest for a hunting trip he undertook in 1913 to (then) Northern Rhodesia. The idea of the chest then gives rise to a variety of forms of healing: from instruments used to exorcise evil spirits and children's letters written to celebrate a heart transplant; to medicinal flowers bought at the Adderley Street flower market. The exhibition aims to visualise and materialise illness and its treatment from historical, cultural and disciplinary perspectives. Drawing on well-established historical and contemporary connections between the disciplines of Botany, Medicine and Pharmacology, the exhibits also suggest latent links which are at times political, at times whimsical. -
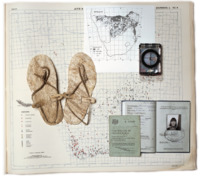
Page 175 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue
"The page presents a curated collection of images: a map from the Avian Demography Unit illustrating the distribution of the bataleur Terathopius ecaudatus along the political border, though the bateleur is more frequently found where there is no formal farming; a Ngwato child’s oxhide sandals collected by Isaac Schapera (a British social anthropologist who worked in South Africa and Botswana); a compass; the identification documents of Paula Ensor (previous dean and Professor of Education), who spent time in exile in Botswana; and a Certificate of Registration necessary for movement across borders, all of which are overlaid on top of a large map from the Afrikaans Atlas provided by Rajend Mesthrie of the Department of Linguistics and Southern African Languages that shows the Afrikaans language’s distribution. Contextualising all of these objects in relation to the large map cuts across disciplinary boundaries and illustrates the scope and impact of the colonial and apartheid regimes and their influence on immigration laws, language studies, ornithology and anthropology" (Liebenberg 2021: 193). -

Pages 38-39 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue
"Objects and collections can reflect naturalisations that occur when the disciplinary perspective renders its subject matter in terms of what it deems worth looking at and how it should be looked at (Daston & Galison 2007: 23). This process has dual consequences, resulting in the honing of a specialised insider focus directed at the object and a blindness to qualities that sit outside the disciplinary frame of reference (as discussed in relation to the Drennan and Kirby collections). 'Curiosity CLXXV' drew on and challenged both these aspects by forcing objects into visual conversations outside their discipline and inviting insiders to view them in these new configurations. These curatorial strategies enabled insiders to become aware of characteristics not normally deemed important in their discipline and to identify the characteristics their discipline did deem important (their attentional subculture, in other words) in objects not studied in their field" (Liebenberg 2021: 180). -

Page 135 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue
"Peering into one of them could, for instance, reveal musical instruments from the South African College of Music’s Kirby collection; old wooden mathematical models of abaci and polyhedrons from the Maths department; mobiles demonstrating platonic solids made by mechanical engineering students; publications by a UCT Professor of Astronomy; a sign pointing to ward D10 from the old section of Groote Schuur Hospital; glass slides once used as a teaching aid for art history at Michaelis; bird ringing material from the Avian Demography unit; and a bottle-brush plant labelled by the son of one of the curators" (Liebenberg 2021: 179). -

Page 65 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue
Page 65 of the 'Curiosity CLXXV' catalogue, showing the Old Anatomy Lecture Theatre (currently part of the Centre for Curating the Archive). -

Page 79 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue.
"Created by Felix von Luschan, an Austrian doctor, anthropologist, explorer, archaeologist and ethnographer in the early 20th century, the chart, known as the Von Luschan chromatic scale (...) was used to classify skin colour and featured as a tool in race studies and anthropometry of the time. Forgotten by its current department staff and students, its presence draws attention to the role of medicine and science in the apartheid agenda and to the larger racist scientific practices of measuring and classifying human physical differences in the 19th and 20th centuries to produce a ‘typology of race’ (Sturken & Cartwright 2018: 351–352). To support such theories, object collections in scientific university departments worldwide also featured collections of human remains; tools for measuring the size and shape of skulls; and charts detailing various physiognomic features (Sturken & Cartwright 2018: 351 – 352)" (Liebenberg 2021: 122 - 125). -

Capitance
"Strategies such as juxtapositioning also served to highlight poetic and emotive qualities in fields not known for encouraging them, as in a cabinet curated by Langerman titled Capitance. This featured a range of instruments from the Physics department used to measure electrical currents (galvanometers, capacitors and Wheatstone bridges); a crystal goniometer measuring crystal face angles and crystal 175 from the crystal collection in Geological Sciences; M.R. Drennan’s models of the human embryo and a wax model of flesh; and a white tutu from the School of Ballet. In combining this selection of scientific instruments with a tutu, Langerman made allowance for the materials to be considered in a more poetic light, inviting the viewer to consider how a grand jeté defies the laws of physics, for example" (Liebenberg 2021: 186). -

Similitude
"In 'Similitude', Langerman brought together a selection of objects from three disparate disciplines – glassware from chemical engineering; a skull with an arrow embedded in it and a torch used as a murder weapon from forensic pathology; and two flutes from the Kirby collection. Ignoring the assigned functions the objects performed within their respective disciplines, she chose instead to use their formal characteristics as a taxonomic device. They were all, as she described them, ‘long thin things’ (Langerman n.d.). In displacing these objects from their respective disciplines and positioning them in proximity to objects that shared this new category, she neutralised their disciplinary functions and flattened their meanings within those fields (Langerman n.d.)" (Liebenberg 2021: 183). -

A display on page 97 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue
"A stainless-steel dilator from the Drennan collection, a carded set of glass slides of xenopus heart sections from the Medical Microbiology collection, a 19th century game called 'Frogs and Toads' from Special Collections and a wax model of an embryo, also from Drennan. This ‘amphibian’-inspired display showcases many qualities of the curatorial method, such as visual quotation (the combination of these materials foregrounds that the shape of the dilator resembles a frog), analogy (the wax embryo, dilator and frogs allude to the resemblance between sperm and tadpoles) and juxtaposition (the frog as a scientific topic dissected and contained in the slides, and the frog as a board piece in a game played by children)" (Liebenberg 2021: 183). -

Page 81 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue.
"At the opening of the Archive and Archive and Public Culture programme (APC) in 2009, Prof. Ndebele stated that ‘there can be no transformation of the curriculum, or indeed of knowledge itself, without an interrogation of archive’, a call which both the Centre for Curating the Archive and the APC have sought to answer by producing scholarship that questions and expands what we understand as ‘archive’ and its relevance in a South African context and in an African university (Skotnes 2019: 21)" (Liebenberg 2021: 195). -

First Encounters
"The caption for the image offered further information about the department in which the medicine chest was located, stating: ‘Black metal travelling medicine chest, containing bottles and packets of medication belonging to Walter Floyd, given to UCT by the Floyd family (Manuscripts and Archives).’ It seemed strange to me that this three-dimensional object would be housed in the Manuscripts and Archives (M&A) department (also known as ‘Special Collections’) of UCT Library, as it hosts collections of ‘printed and audio-visual materials on African studies and a wide array of other specialised subjects, as well as over 1,300 sub-collections of unique manuscripts and personal papers’ (Special Collections 2015). As my italics emphasise, bulkier three-dimensional objects seemed to have no place here. I nonetheless thought it worthwhile to type the words ‘medicine chest’ into the general library search engine, an application called Ex Libris Primo; the search delivered no results" (Liebenberg 2021: 24). -

Curiosity CLXXV
Hiddingh Hall during the construction of the installation of Curiosity CLXXV. -

Hiddingh Hall
Hiddingh Hall prior to the installation of Curiosity CLXXV. -

Resonance (Greenblatt)
In 'Resonance and Wonder' Greenblatt discusses ‘resonant’ moments in regards to museum displays as “those in which the supposedly contextual objects take on a life of their own and make a claim that rivals that of the object that is formally privileged. A table, a chair, a map – often seemingly placed only to provide a decorative setting for a grand work – become oddly expressive, significant not as a background but as compelling representational practices in themselves. These practices may in turn impinge on the grand work, so that we begin to glimpse a kind of circulation: the cultural practice and social energy implicit in mapmaking is drawn into the aesthetic orbit of a painting, which has itself enabled us to register some of the representational significance of the map” (1991: 22- 23). For him a resonant exhibition often “pulls the viewer away from the celebration of isolated objects and toward a series of implied, only half-visible relationships and questions” (1991: 23). -

Resonance
Image from page 137 of the 'Curiosity CLXXV' catalogue, describing resonance and its application in MRI technology. -

175 chalk-board dusters
For the exhibition, 'Curiosity CLXXV', the curators took an old duster from each teaching venue and replaced it with a new one. -

Iroko
Structurally, 'Chest: a botanical ecology' consisted of 15 modular interlocking cabinets of differing sizes which rested on top of one another, making up the front of the display. These were constructed from two types of wood, the darker iroko wood, and a lighter ash wood – with the iroko originating from the repurposed cabinets used for Curiosity CLXXV in 2004. The Iroko tree is a large hardwood tree from the west coast of tropical Africa, known by the Yoruba as ìrókò, logo or loko. Believed to have supernatural properties, it can live up to 500 years. Yoruba people believe that a spirit inhabits the tree, and anybody who sees the Iroko-man face to face becomes insane and dies. According to the Yoruba, any man who cuts down any Iroko tree causes devastating misfortune on himself and all of his family. In West Africa, the iroko wood is also used to make the djembe drum. If they however, need to cut down the tree, they can make a prayer afterwards to protect themselves. Used for a variety of purposes including boat-building, domestic flooring, furniture and outdoor gates, from the late 1990s, it was also used as part of the txalaparta, a Basque musical instrument constructed of wooden boards, due to its lively sound and classified as an idiophone (a percussion instrument) (Ogumfe 1929: online)).


