Items
Site
The Medicine Chest
keywords is exactly
Wellcome Library
-

Tabloid medicine chest from Scott Polar Expedition
The expedition carried with them a Tabloid Medicine Chest. On the 11th of March, knowing that the party was unlikely to survive, Scott ordered Edward Wilson, the expedition’s Chief Scientist and a qualified doctor, to divide the painkillers between them so they could each end their life on their own terms. Writing in his diary on that day, Scott states, “I practically ordered Wilson to hand over the means of ending our troubles to us, so that anyone of us may know how to do so". Scott, Bowers and Oates had thirty opium tabloids apiece and Wilson, the morphine. Scotts diary entry on either the 22nd or 23rd of March showed that they had a change of heart however: “no fuel and only one or two left of food — must be near the end. Have decided that it shall be natural — we shall march for the depot with or without our effects and die in our tracks". -

The hut
Captain Scott writes in his den in the Terra Nova hut in this October 7, 1911. -

Your inner fish
"Our hands resemble fossil fins; our heads are organised like those of long extinct jawless fish and major parts of our genomes still look and function like those worms and bacteria" (Shubin 2008). During the summer of his second year of study, paleontologist and evolutionary biologist, Neil Shubin, discovered a particular fossil fish in the Arctic, naming it the Tiktaalik. In Your Inner Fish: A Journey into the 3.5-Billion-Year History of the Human Body (2009) he explored the connections in our human anatomy with those fishes that ventured onto land over 375 million years ago, based on the information gathered from studying the Tiktaalik. -
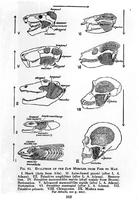
Of fish and men
The evolution of jaw muscles from fish to men. -

Barkly Bridge over the Vaal River and a barge
Woodburytype -

Devils Bridge sketched by Lister
'Devils Bridge' sketched by Lister on his travels through Europe showing a bridge crossing the Gotthard Pass, northern approach, Switzerland. The term 'devil's bridge' is applied to many ancient bridges found primarily in Europe. These were stone or masonry arch bridges and, because they represented a significant technological achievement in ancient architecture, were objects of fascination and stories. The most popular of these featured the Devil, either as the builder of the bridge (relating to the precariousness or impossibility of such a bridge to last or exist in the first place) or as a pact-maker (sharing the necessary knowledge to build the bridge, usually in exchange for the communities souls). The legend attached to the bridge sketched by Lister is of the latter, and was related by Johann Jakob Scheuchzer in 1716. According to Scheuchzer, the people of Uri recruited the Devil for the difficult task of building the bridge. In return for his expertise, the Devil requested the soul of the first thing to pass the bridge. To trick the Devil, the people of Uri sent across a dog by throwing a piece of bread, and the dog was promptly torn to pieces by the Devil. Reference: Scheuchzer, J. , 1747 [1716]. Naturgeschichte des Schweitzerlandes. Vol. 2: 94. -

Micrographia
Engraving, magnified view of the forms of small diamonds or shining sparks in flints (fig. 1), "the forms of gravel in urine (fig. 2), and a variety of regular for resulting from various combinations of globules (fig. 3, 4)"; Schem. 5. From 'Micrographia: or some physiological descriptions of minute bodies made by magnifying glasses with observations and Inquiries thereupon' by Robert Hooke, Fellow of the Royal Society, 1665. -

Silicosis
A gold miner using a rock drill with a water spray in an attempt to prevent the occupational disease silicosis, caused by dust inhalation.


