Items
Site
The Medicine Chest
keywords is exactly
apartheid
-

Miscast (installation detail)
Instruments from the Kirby collection displayed as part of the 'Miscast' exhibition. -

Miscast (Lane reflects)
"Where viewers had to walk over a floor of vinyl tiles printed with photocopied newspaper articles and photographs of the San, Lane reflected on another archaeological parallel: ‘just as the texts and images on the floor represent the debris of a particular history, so too do the artefacts strewn across the surface of a site’ (Lane 1996: 7). Yet in trying to define sites and their history, archaeologists feel ‘they can tread on the debris of their own or others’ ancestors with equanimity, colonizing that space for themselves’ (Lane 1996: 7)" (Liebenberg 2021: 172 - 174). -

Miscast (installation detail)
"In juxtaposing instruments that are still being used (such as the scalpel and the camera) with ones that are not (the Von Luschan skin colour chart and the anthropometric measuring rods), Skotnes set up an opportunity for science to reflect on its past and on the activities and objects of its present, enabling a mode of self-reflexivity that is not a standard part of its day-to-day practices. Through curatorship, she exposed disciplinary practitioners to naturalisations and blind spots within their fields and sensitised them to these previously occluded characteristics" (Liebenberg 2021: 172). -

Page 79 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue.
"Created by Felix von Luschan, an Austrian doctor, anthropologist, explorer, archaeologist and ethnographer in the early 20th century, the chart, known as the Von Luschan chromatic scale (...) was used to classify skin colour and featured as a tool in race studies and anthropometry of the time. Forgotten by its current department staff and students, its presence draws attention to the role of medicine and science in the apartheid agenda and to the larger racist scientific practices of measuring and classifying human physical differences in the 19th and 20th centuries to produce a ‘typology of race’ (Sturken & Cartwright 2018: 351–352). To support such theories, object collections in scientific university departments worldwide also featured collections of human remains; tools for measuring the size and shape of skulls; and charts detailing various physiognomic features (Sturken & Cartwright 2018: 351 – 352)" (Liebenberg 2021: 122 - 125). -

Miscast (instruments of measurement)
"Along with the guides that regulated practices and protocols to stabilise and standardise an individual’s response to unfamiliar and disorienting sights (Kennedy 2013: 42), the gender, class and ethnicity of the observer were also of importance , as was the use of ‘ever more sophisticated instruments and calculations designed to minimize the intrusion of subjectivity into the reporting of information’ (Driver 2001: 55). By regulating who was doing the viewing, stipulating what should be viewed and how and supplying tools to measure these observations, scientific institutions promoted an authoritative ‘way of seeing’ in the field that differentiated the scientific view from that of the ordinary traveller (Driver 2001: 49)" (Liebenberg 2021: 109). -

Pattern recognition
A display in Groote Schuur Hospital, Cape Town. The label reads: The History of Crockery Apartheid did more than separate the races. Parallel with the separate crockery for the different religions (Jewish = Blue; Muslim = Pink) was a range of separate crockery for the staff and patients of different races. Here are a few examples of this complex collection: Royal Blue: Jewish patients and staff (kosher) Dark Navy Blue: "European" patients Green: "European" staff Maroon: "Non European" patients Black: "Non European" staff Pink: Muslim patients and staff (halaal) These pieces of crockery are now part of our history and all patients are served meals in the standard rectangular crocker plate. -

Skin
I collected leaves from the gardens around Groote Schuur Hospital and gave them to UCT dermatologist Ranks Lehloenya for analysis. Using the strategy of directing insider focus to an outsider object, Lehloenya treated these specimens as sections of skin and read them accordingly, highlighting sections that showed signs of nummular eczema, acne, ageing, miliary tuberculosis and melanoma, to name a few (Liebenberg 2021: 277). This example was diagnosed as follows: "This section shows characteristics which could point at various causes. The darker raised sections could be blackheads as seen in acne (note the darker central area reminiscent of an open pore); villous hair cysts ( a condition in which hair follicles are trapped under the skin to form pimple-like structures with the hair giving a dark hue in the centre; syringomas (non-cancerous proliferation of sweat glands); infections such as chicken pox or miliary tuberculosis in which the infection spreads from the blood onto the skin (miliary mean it looks like a millet seed). It could also be metastatic melanoma that has spread from another area onto this skin". -
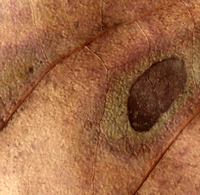
Skin
I collected leaves from the gardens around Groote Schuur Hospital and gave them to UCT dermatologist Ranks Lehloenya for analysis. Using the strategy of directing insider focus to an outsider object, Lehloenya treated these specimens as sections of skin and read them accordingly, highlighting sections that showed signs of nummular eczema, acne, ageing, miliary tuberculosis and melanoma, to name a few (Liebenberg 2021: 277). This example exhibits an annular pattern which could be an infection like a ringworm (fungus) and erythema migrans of Lyme’s disease; or inflammatory conditions like nummular eczema, erythema marginatum as seen in rheumatic fever and granuloma annulare. -

1975 (Invasive Species)
1975 (Invasive Species) stems from a historical and botanical enquiry. In 1975, after attaining independence from Portugal, the civil war broke out in Angola. In that same year, the South African Defense Force under the authorization of Vorster, intervened in the war – an intervention which formed part of an ongoing period of conflict in South African history, known as the Border Wars. From a botanical point of departure, the cluster pine (or Pinus Pinaster) is native to Portugal. In South Africa it is seen as invasive, competing with and replacing indigenous species. The work consists of a cross section of cluster pine used as a target practice unit, into which the artist shot a ring of R4 assault rifle bullets – aiming at tree ring 1975.


