Items
Site
The Medicine Chest
keywords is exactly
cancer
-

Simone
A year after Simone's death from cancer, Cousteau announced that he had been having an affair with a woman, Francine Triplet, for over a decade. He also had two children with her, Diane and Pierre-Yves. -

Melchior & Cousteau
In 1963 Simone Melchior became the world's first female aquanaut by living in Starfish House, an underwater habitat, for the final four days of the Conshelf II project. Although never visible in the 'Undersea World of Jacques Cousteau' series, Cousteau's wife and business partner played a key role in the operation at sea. She was the acting mother, healer, nurse and psychiatrist to the all-male crew for 40 years. Cousteau describes her as being "happiest out of camera range, in the crow’s nest of the Calypso (...), scanning the sea for whales". Her father, Henri Melchior, was director of Air Liquide (France’s main producer of industrial gases at the time) and funded the invention of the aqua lung and the scuba diving apparatus we know today. -

Four bruises
Poster designed by film director, Mike Mills. His 2010 movie, 'Beginners', is structured as a series of interconnected flashbacks. Following the death of his father, Hal, from cancer, Oliver reflects on their relationship during the last five years, since the death of his mother. -

Skin
I collected leaves from the gardens around Groote Schuur Hospital and gave them to UCT dermatologist Ranks Lehloenya for analysis. Using the strategy of directing insider focus to an outsider object, Lehloenya treated these specimens as sections of skin and read them accordingly, highlighting sections that showed signs of nummular eczema, acne, ageing, miliary tuberculosis and melanoma, to name a few (Liebenberg 2021: 277). This example was diagnosed as follows: "This section shows characteristics which could point at various causes. The darker raised sections could be blackheads as seen in acne (note the darker central area reminiscent of an open pore); villous hair cysts ( a condition in which hair follicles are trapped under the skin to form pimple-like structures with the hair giving a dark hue in the centre; syringomas (non-cancerous proliferation of sweat glands); infections such as chicken pox or miliary tuberculosis in which the infection spreads from the blood onto the skin (miliary mean it looks like a millet seed). It could also be metastatic melanoma that has spread from another area onto this skin". -
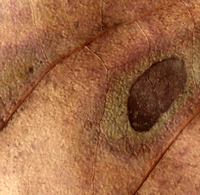
Skin
I collected leaves from the gardens around Groote Schuur Hospital and gave them to UCT dermatologist Ranks Lehloenya for analysis. Using the strategy of directing insider focus to an outsider object, Lehloenya treated these specimens as sections of skin and read them accordingly, highlighting sections that showed signs of nummular eczema, acne, ageing, miliary tuberculosis and melanoma, to name a few (Liebenberg 2021: 277). This example exhibits an annular pattern which could be an infection like a ringworm (fungus) and erythema migrans of Lyme’s disease; or inflammatory conditions like nummular eczema, erythema marginatum as seen in rheumatic fever and granuloma annulare. -

Tobacco Mosaic Virus
During the late 19th century, tobacco farmers observed a strange occurrence on the leaves of their tobacco plants. A mosaic pattern of light and dark green (or yellow and green, in some instances) appeared on the leaves of their crops, the presence of which signalled the steady decline in the plant’s growth. Because of the lucrative nature of the industry, finding a treatment for this seemingly infectious disease became a priority, with many laboratories working to isolate the cause. Bacteria were recognised as the causative agents of many infectious diseases of plants and animals, including humans, in the second half of the 19th century – and the technique of filtration was developed to separate infectious agents from extracts or exudates in order to study these microbes. It was whilst utilising this technique that Dmitri Ivanovski, a Russian microbiologist working in the Crimea in 1890, made a surprising discovery. Using the Chamberland–filter made from porcelain and designed to trap ordinary bacteria, Ivanovsky discovered that the filtered sap from the diseased plants could continue to transfer the infection to healthy plants – an occurrence he attributed to an agent which must be an exceedingly small parasitic microorganism, invisible even under great magnification. It would take another 45 years before the visualisation of this subcellular entity would be formulated with the help of an electron microscope, but Ivanovksy, along with the Dutch botanist M.W. Beijerinck, who also and independently, isolated these microbes in his laboratory in 1898, are generally credited for the discovery of viruses. The disease which infected the tobacco plants would be aptly called the Tobacco Mosaic Virus, and its identification would signal the initiation of a field of study known as virology.


