Items
Site
The Medicine Chest
keywords is exactly
instruments
-

Healing instruments
“I invited Edmund February to the Kirby collection to view the instruments and learn his thoughts on them from a botanical perspective. February identified the dancing rattles as being made of the seed pods of Oncoba spinosa (Venda: mutuzwa) and the seed pod of Adansonia digitata (Venda: muvhuyu). The wood of the iodophone was, however, unrecognisable as a result of its handling. February also contacted colleagues in the Department of Zoology and the School of Mathematical & Natural Sciences at the University of Venda, who connected me to a Venda diviner, Muanalo Dyer, who uses similar baobab rattles (and other materials from that tree) in her healing practices. This interdisciplinary engagement showed that these instruments, supposedly frozen in their early 20th century understanding of being on the brink of extinction, remained very much functional in the present” (Liebenberg 2021: 271). -

Isigubu through Gqom
"In 2018, the Zulu drum alleged to have been played during the 1906 Bambatha rebellion against British rule and unfair taxation in the colony of Natal (discussed by Nixon) became the focus of Amogelang Maledu’s Honours research project. In ‘Isigubu through gqom: The sound of defiance and Black joy’, Maledu (who has an undergraduate degree in Anthropology and Visual Culture) used the drum’s history of colonial resistance and contextualised it through the contemporary musical genre of gqom, showing music as both an act and celebration of joy and freedom and of defiance against the limitations of township life. Through her ‘speculative and imagined interconnectedness’ of the isigubu and gqom, Maledu appropriated the limited information available about the former and expanded it by reinventing new historical pathways that reframed colonial narrations and aesthetics (Maledu 2018: 29–30). Her curation broke the silence of the Kirby instruments and liberated the isigubu from its ethnomusicological framework through a juxtaposition that spoke back to history and the contemporary moment. In addition, a website provides a framework for historicising gqom and encouraged the growth of its archive through viewer engagement, also highlighting the speculative and stagnant colonial archive in which the isigubu is situated (Maledu 2018: 29–30)" (Liebenberg 2021: 211 - 212). -

Etching from 'Sound from the Thinking Strings'
"Skotnes’s own visual interpretation of the history and cosmology of the |xam formed the last component of this interdisciplinary endeavour and constituted a visual component that drew together the various strands of disciplinary interpretations and presented a perspective on the |xam life she felt ‘was missing from the other interpretations’ (Skotnes 1991: 30). In these images she drew freely on San mythology, accounts of |xam life recorded by Lucy Lloyd, historical and archaeological research and images from rock paintings in a landscape setting. She writes in her preface that these etchings were direct attempts at ‘inverting the museum dioramas’ in the ethnographic halls close to the exhibition and which, through their display of the San’s body casts, rendered them closer to specimens of biology than as members of a highly developed culture (Skotnes 1991: 52). By creating images that combined shamanistic rituals, entoptic spirals, plants, hunting bags, bows and arrows, snakes, eland-shaped rainclouds, colonists, musical instruments, shelters and therianthropic shapes, Skotnes eclipsed the static narratives of the dioramas and the object labels in the exhibition, placing them in a context in which their metaphysical qualities were celebrated more than their physical qualities. These prints stood in striking contrast to the other exhibits, which framed the San as physical types, and they challenged viewers to confront the reality that the San had a rich history and cultural and social life" (Liebenberg 2021: 157). -

Sound from the Thinking Strings (installation detail)
"Skotnes had a longstanding relationship with the museum, which started when she was still a student at the Michaelis School of Fine Art. Davison remembers that Skotnes would visit the taxidermy section of the South African museum to draw bones. As an anthropologist, Davison admits to finding Skotnes’s way of looking at things stimulating – an individual way of looking at objects that made her look at them differently, even though she was already very familiar with these materials. Davison recalls a visit to the ethnographic stores during which she showed Skotnes the San skin bags, carefully conserved in their drawers and laid out on acid-free paper. Skotnes admired not only their aesthetic qualities but related the stories she had been studying in the Bleek and Lloyd archive to them – stories that shifted their status from anthropological museum objects to powerful animate objects in San spiritual and social life (P. Davison, personal communication, 28 January 2021). Skotnes remembers that she asked staff whether they knew what was inside the bags and was shocked when nobody could remember looking in them. She was allowed to look inside one and found a claw, which they thought must be a leopard’s (P. Skotnes, personal communication, 9 May 2021)" (Liebenberg 2021: 2015). -

Miscast (installation detail)
Instruments from the Kirby collection displayed as part of the 'Miscast' exhibition. -

Page 135 of the Curiosity CLXXV catalogue
"Peering into one of them could, for instance, reveal musical instruments from the South African College of Music’s Kirby collection; old wooden mathematical models of abaci and polyhedrons from the Maths department; mobiles demonstrating platonic solids made by mechanical engineering students; publications by a UCT Professor of Astronomy; a sign pointing to ward D10 from the old section of Groote Schuur Hospital; glass slides once used as a teaching aid for art history at Michaelis; bird ringing material from the Avian Demography unit; and a bottle-brush plant labelled by the son of one of the curators" (Liebenberg 2021: 179). -

The Kirby collection of musical instruments
"Kirby’s choice of an ‘age-old simple classification’ to order the instruments can be correlated with another classification formulated at Wits around the time he was collecting. The Department of Bantu Studies was established in the 1920s at roughly the same time as the Music Department. Kirby’s use of the phrase ‘native races’, which features in the title of his book, resonates with the descriptive subtitle of the Wits journal connected to research in this department: Bantu Studies: A Journal Devoted to the Scientific Study of Bantu, Hottentot, and Bushman (Nixon 2013: xii). The homogenising act of categorising all diverse indigenous South African groups into three general categories seems to echo Kirby’s taxonomic imposition on the diverse instruments he collected on his trips and that continues to feature as the ordering principle of this collection" (Liebenberg 2021: 136). -

Miscast (installation detail)
"In juxtaposing instruments that are still being used (such as the scalpel and the camera) with ones that are not (the Von Luschan skin colour chart and the anthropometric measuring rods), Skotnes set up an opportunity for science to reflect on its past and on the activities and objects of its present, enabling a mode of self-reflexivity that is not a standard part of its day-to-day practices. Through curatorship, she exposed disciplinary practitioners to naturalisations and blind spots within their fields and sensitised them to these previously occluded characteristics" (Liebenberg 2021: 172). -

Capitance
"Strategies such as juxtapositioning also served to highlight poetic and emotive qualities in fields not known for encouraging them, as in a cabinet curated by Langerman titled Capitance. This featured a range of instruments from the Physics department used to measure electrical currents (galvanometers, capacitors and Wheatstone bridges); a crystal goniometer measuring crystal face angles and crystal 175 from the crystal collection in Geological Sciences; M.R. Drennan’s models of the human embryo and a wax model of flesh; and a white tutu from the School of Ballet. In combining this selection of scientific instruments with a tutu, Langerman made allowance for the materials to be considered in a more poetic light, inviting the viewer to consider how a grand jeté defies the laws of physics, for example" (Liebenberg 2021: 186). -

Similitude
"In 'Similitude', Langerman brought together a selection of objects from three disparate disciplines – glassware from chemical engineering; a skull with an arrow embedded in it and a torch used as a murder weapon from forensic pathology; and two flutes from the Kirby collection. Ignoring the assigned functions the objects performed within their respective disciplines, she chose instead to use their formal characteristics as a taxonomic device. They were all, as she described them, ‘long thin things’ (Langerman n.d.). In displacing these objects from their respective disciplines and positioning them in proximity to objects that shared this new category, she neutralised their disciplinary functions and flattened their meanings within those fields (Langerman n.d.)" (Liebenberg 2021: 183). -

Rattles in the Kirby collection
A drawer of rattles in the South African College of Music's Kirby collection: "The instruments are now grouped in different cabinets according to the taxonomy set out by Kirby in his book. In the preface to the second edition (1964), Kirby shares some of his considerations when deciding how to group the instruments, writing that he had to decide ‘whether to arrange his material tribally, or to deal with each type of musical instrument separately from the technological and historical points of view, allowing the tribal aspects to emerge incidentally’ (Kirby 1964: xi). Kirby chose the second alternative, stating that his chief reason was that he wanted the work to be, as far as possible, ‘a complete and comparative study of one particular aspect of the life of our aborigines’ (1964: xi). His second consideration was to find the most suitable manner for classifying the instruments, for which he defaulted to the ‘age-old simple classification of musical instruments into three main groups of percussion, wind and strings’ (1964: xi) – a Western system for the classification of instruments and the principles on which they were based. The chapters in his book and the displays in the room are thus grouped into three categories: percussion – ‘rattles and clappers’, ‘drums’, ‘xylophones and sansas’ and ‘bull-roarers and spinning-disks’; wind instruments – ‘horns and trumpets’, ‘whistles, flutes, and vibrating reeds’ and ‘reed flute ensembles’; and stringed instruments – ‘stringed instruments’ and ‘Bushmen and Hottentot violins and the ramkie’. Kirby encountered one taxonomic anomaly when employing this system: the ‘gora’, an instrument both wind and string, which he termed ‘a stringed-wind instrument’" (Liebenberg 2021: 135). -

Miscast (instruments of measurement)
"Along with the guides that regulated practices and protocols to stabilise and standardise an individual’s response to unfamiliar and disorienting sights (Kennedy 2013: 42), the gender, class and ethnicity of the observer were also of importance , as was the use of ‘ever more sophisticated instruments and calculations designed to minimize the intrusion of subjectivity into the reporting of information’ (Driver 2001: 55). By regulating who was doing the viewing, stipulating what should be viewed and how and supplying tools to measure these observations, scientific institutions promoted an authoritative ‘way of seeing’ in the field that differentiated the scientific view from that of the ordinary traveller (Driver 2001: 49)" (Liebenberg 2021: 109). -
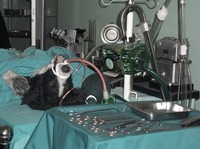
Dogs in the Heart of Cape Town
The guided tour of the museum, which commemorates the first heart transplant performed by Chris Barnard in 1967, starts with a representation of the car accident that provided the heart for the transplant, through to the animal lab where Barnard conducted experiments with over 50 dogs to perfect the technique of heart transplantation. From there one can tour a model of Denise Darvall's bedroom and Christiaan Barnard's office before seeing a recreation of the surgery in the actual operating theaters where it occurred. -

Navigation chart, Micronesia
"Early Pacific seafarers did not have scientific instruments or conventional European-style maps to voyage to, and settle, the thousands of islands of Micronesia and Polynesia. Instead they used the movement of the sea, the direction of the wind, the position of the sun and stars, and the flight of birds. This is a navigation chart, obtained by Georg Irmer, the Governor of the Marshall Islands from Chief Nalu of Jaluit atoll in 1896. The strips of wood, bound by cane, represent the currents and winds, and the six small, white shells represent islands". -

About Ed Ricketts
"Just about dusk one day in April 1948 Ed Ricketts stopped work in the laboratory in Cannery Row. He covered his instruments and put away his papers and filing cards. He rolled down the sleeves of his wool shirt and put on the brown coat which was slightly small for him and frayed at the elbows. He wanted a steak for dinner and he knew just the market in New Monterey where he could get a fine one, well hung and tender. He went out into the street that is officially named Ocean View Avenue and is known as Cannery Row. His old car stood at the gutter, a beat-up sedan. The car was tricky and hard to start. He needed a new one but could not afford it at the expense of other things. Ed tinkered away at the primer until the ancient rusty motor coughed and broke into a bronchial chatter which indicated that it was running. Ed meshed the jagged gears and moved away up the street. He turned up the hill where the road crosses the Southern Pacific Railways track. It was almost dark, or rather that kind of mixed light and dark which makes it very difficult to see. Just before the crossing the road takes a sharp climb. Ed shifted to second gear, the noisiest gear, to get up the hill. The sound of his motor and gears blotted out every other sound. A corrugated iron warehouse was on his left, obscuring any sight of the right of way. The Del Monte Express, the evening train from San Francisco, slipped around from behind the warehouse and crashed into the old car. The cow-catcher buckled in the side of the automobile and pushed and ground and mangled it a hundred yards up the track before the train stopped" (Steinbeck 1951: 279). After Ricketts' death in 1948, Steinbeck dropped the species catalogue from the earlier 'The Sea of Cortez' and republished it with a eulogy to his friend added as an afterword. -

Kuhn's Jellyfish
Kuhn's "example illustrates how the entrenched expectations of experimental outcomes and prescribed instrumental functions of an insider’s view of the laboratory and its equipment can pose a threat to new discoveries. The circumstances that enabled Roentgen (an insider) to first notice these new rays are not clear, but Kuhn proposes that the occurrence of anomaly enables discovery and that Roentgen’s ‘recognition that nature has somehow violated the paradigm-induced expectations that govern normal science’ (1970: 52–3) was important. Kuhn emphasises that Roentgen valued the anomaly instead of ignoring it – a vital step in the process of discovery" (Liebenberg 2021: 114). -

End papers of 'What to Observe'
Published in 1841, Jackson’s guide was the first of a series of guides published during this period which offered notes for the traveller on appropriate conduct in the field – from providing methods for training the eye to observe what was deemed as relevant details, to instructions on which precision instruments should be carried and how to use them to record and inscribe the results of observations made (Withers 2013: 170). As Jackson states, his guide pointed out to the “uninitiated Traveller what he [sic] should observe, and to remind the one who is well informed, of many objects which (…) might escape him” (Jackson 1841: i). -

Heart of Cape Town Museum
Christiaan Barnard did forty-eight trial transplants with dogs before he undertook such an operation with a human being. -

Bird Mark 7 Respirator
Dr. Bird invented a number of popular medical devices that were used to care for patients with breathing problems. During WWII he served in the Army Air Corps where, in addition to training and transport assignments, he studied aircraft and respiratory and cardiovascular problems at high altitude. Two devices that he produced during the war went into the design of his first commercial ventilator, the Mark 7 Respirator. Dr. Bird’s respirators and anesthesia ventilators have been used during many of the first human surgical procedures. Among these were the first open heart procedure and the first liver transplant. -

SP-368 Biomedical Results of Apollo
Electrocardiograph signal received at Mission Control during various periods of the Apollo 11 mission -

Avoided Object
Photographs of the sky above the Imperial War Museum taken with the camera that belonged to Hoess, commandant of Auschwitz


