Items
Site
The Medicine Chest
keywords is exactly
pathology
-

A 'Jungle'
"A ‘jungle’ consisted of a selection of pathological specimens from the Pathology Learning Centre that had been affected by typhoid fever, ascaris adult worms, yellow fever, amoebic ulcerations, tuberculosis and malaria. The diseases that afflicted these specimens were regarded as ‘tropical’. As described in Chapter One, BWC used the jungle as a significant terrain that called for a medicine chest to combat pathogens: ‘Whether you were valiantly saving your compatriot in war, traversing a dark African jungle, navigating one of the world’s first flying machines, exploring the most desolate place on earth, ascending the highest mountain in the world, or simply enjoying the windswept British coast, the chest would be there, ready for any ailment’ (Johnson 2008b: 255). BWC promoted their chests as the ideal antidote for a tropical landscape ‘at once full of potential wealth for imperial Britain, but simultaneously rife with disease’ (Johnson 2008b: 258) and claimed that the tropical colonies were ‘by far the most dangerous regions for travellers’ (BWC 1934: 8). It was here that ‘desolating ailments’ were encountered, all ‘particularly fatal to the so-called white man who originates in temperate climates’ (BWC 1934: 8). I adapted the colour of the images of afflicted intestines, livers, stomachs and brains and used them as material to construct a dense jungle that referenced this aspect of the medicine chest’s history. Printed on separate glass sections that fit into the cabinet at spaced intervals to create an illusion of depth and three-dimensionality, the work draws on the cross-sectional display technique used in many anatomy museums worldwide, in projects such as the Visible Human Project (1995) and that the artist Damien Hirst references in his works . Creating a visual link between the UCT specimens and the history of these diseases surfaces the occluded racial undertones of these understandings" (Liebenberg 2021: 267). -

Subtle Thresholds (PLC)
"Integrated into the PLC, these works speak to the specimens on display and provide interesting access points to the collection. The animal-faeces prints (which referenced ‘sites of contamination’ in the context of the SAM exhibition) resonate, for instance, with many of the specimens on display in the PLC, such as the heterotopic heart (also called a ‘piggy-back heart transplant’) created by Dr Chris Barnard in 1977, consisting of a baboon heart grafted onto a human heart for additional motoric support. In addition to their more ‘famous’ specimens, the centre also has an extensive intestinal worm collection and many organs affected by zoonotic diseases, such as a liver ravaged by malaria. This was not a conscious decision on the part of the artist-curator and illustrates how curation can draw attention to aspects of a collection and liberate new associations when brought into conversation with it" (Liebenberg 2021: 201). -
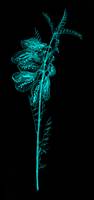
Planthology (detail)
“For 'Planthology (Bulbine frutescens and Lessertia frutescens)' I sourced two medicinal plant specimens from Kirstenbosch National Botanical Garden and x-rayed them at Groote Schuur Hospital (#10 and #13). These two local plants offer a wide variety of healing properties and address the lacuna of the chest. The fresh leaves of the Bulbine frutescens produce a jelly-like juice that can be used for burns, rashes, blisters, insect bites, cracked lips, acne, cold sores, mouth ulcers and areas of cracked skin, while an infusion of these leaves in a cup of boiling water can be taken for coughs, colds and arthritis (Harris 2003: online). The Lessertia frutescens is used as an immune booster in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, as a medicine in the treatment of chicken pox, internal cancers, colds, asthma, TB, bronchitis, rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, liver problems, haemorrhoids, piles, bladder and uterus problems, diarrhoea, dysentery, stomach ailments, heartburn, peptic ulcers, backache, diabetes, varicose veins and inflammation (Xaba & Notten 2003: online)” (Liebenberg 2021: 269). -

Planthology
In conversation with Dr Yeats in 2011 about adding a few medicinal plants to the centre as part of its displays, she mentioned that no plants survived in there. They all seemed to die from some mysterious cause. I decided to source three medicinal plants, the Lessertia frutescens, Bulbine frutescens and Artemisia afra, and X-ray them to 'diagnose' what might be the cause of their demise. In subjecting the plants to this process and placing the x-ray images in a space that foregrounds the diagnosis of human disease, I intended to create a heterarchical shift in this relationship, considering a world in which the degree of care directed toward human ailments might be replicated in treating diseases manifest in the botanical world. -

Hosts and Carriers
A selection of glass slides of the insects, ticks and worms that are the primary or intermediate hosts or carriers of human diseases. These slides also featured in the 'Curiosity CLXXV' and 'Subtle thresholds' exhibitions, sourced from the Pathology Learning Centre (PLC), where they were originally donated by the secretary of the Department of Microbiology. Dr Yeats identified them as glass photomicrographs and speculated that they were probably made for a special projector used for teaching many years ago.


