Items
Site
The Medicine Chest
keywords is exactly
science
-

Miscast (Lane reflects)
"Where viewers had to walk over a floor of vinyl tiles printed with photocopied newspaper articles and photographs of the San, Lane reflected on another archaeological parallel: ‘just as the texts and images on the floor represent the debris of a particular history, so too do the artefacts strewn across the surface of a site’ (Lane 1996: 7). Yet in trying to define sites and their history, archaeologists feel ‘they can tread on the debris of their own or others’ ancestors with equanimity, colonizing that space for themselves’ (Lane 1996: 7)" (Liebenberg 2021: 172 - 174). -

Miscast (installation detail)
"In juxtaposing instruments that are still being used (such as the scalpel and the camera) with ones that are not (the Von Luschan skin colour chart and the anthropometric measuring rods), Skotnes set up an opportunity for science to reflect on its past and on the activities and objects of its present, enabling a mode of self-reflexivity that is not a standard part of its day-to-day practices. Through curatorship, she exposed disciplinary practitioners to naturalisations and blind spots within their fields and sensitised them to these previously occluded characteristics" (Liebenberg 2021: 172). -

Diary of an oologist
"In 2019, Honours in Curatorship student Nathalie Viruly, who completed her Bachelor of Social Science in Politics and Sociology, was similarly struck by the silence and loss evoked by the [Peter Steyn] collection. Viruly honed in on the moments documented in the notebooks, which capture the loss of life in the reproductive life of these birds and reveal ‘stories of avian tragedy’: Young taken by predator; 1 young accidentally killed; 2 eggs failed to hatch; 2 infertile; Chick disappeared without a trace; Eggs disappeared; Literally cooked by the [corrugated] roof; Nest empty – egg collectors? (Viruly 2018: online). Her focus on these moments in the scientific journal poignantly reveals the conflation between science and emotion and invites the viewer to re-examine hierarchies of loss" (Liebenberg 2021: 219). -

Miscast (instruments of measurement)
"Along with the guides that regulated practices and protocols to stabilise and standardise an individual’s response to unfamiliar and disorienting sights (Kennedy 2013: 42), the gender, class and ethnicity of the observer were also of importance , as was the use of ‘ever more sophisticated instruments and calculations designed to minimize the intrusion of subjectivity into the reporting of information’ (Driver 2001: 55). By regulating who was doing the viewing, stipulating what should be viewed and how and supplying tools to measure these observations, scientific institutions promoted an authoritative ‘way of seeing’ in the field that differentiated the scientific view from that of the ordinary traveller (Driver 2001: 49)" (Liebenberg 2021: 109). -

Your inner fish
"Our hands resemble fossil fins; our heads are organised like those of long extinct jawless fish and major parts of our genomes still look and function like those worms and bacteria" (Shubin 2008). During the summer of his second year of study, paleontologist and evolutionary biologist, Neil Shubin, discovered a particular fossil fish in the Arctic, naming it the Tiktaalik. In Your Inner Fish: A Journey into the 3.5-Billion-Year History of the Human Body (2009) he explored the connections in our human anatomy with those fishes that ventured onto land over 375 million years ago, based on the information gathered from studying the Tiktaalik. -
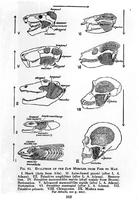
Of fish and men
The evolution of jaw muscles from fish to men. -

Resonance (Greenblatt)
In 'Resonance and Wonder' Greenblatt discusses ‘resonant’ moments in regards to museum displays as “those in which the supposedly contextual objects take on a life of their own and make a claim that rivals that of the object that is formally privileged. A table, a chair, a map – often seemingly placed only to provide a decorative setting for a grand work – become oddly expressive, significant not as a background but as compelling representational practices in themselves. These practices may in turn impinge on the grand work, so that we begin to glimpse a kind of circulation: the cultural practice and social energy implicit in mapmaking is drawn into the aesthetic orbit of a painting, which has itself enabled us to register some of the representational significance of the map” (1991: 22- 23). For him a resonant exhibition often “pulls the viewer away from the celebration of isolated objects and toward a series of implied, only half-visible relationships and questions” (1991: 23). -

Resonance
Image from page 137 of the 'Curiosity CLXXV' catalogue, describing resonance and its application in MRI technology. -

Devils Bridge sketched by Lister
'Devils Bridge' sketched by Lister on his travels through Europe showing a bridge crossing the Gotthard Pass, northern approach, Switzerland. The term 'devil's bridge' is applied to many ancient bridges found primarily in Europe. These were stone or masonry arch bridges and, because they represented a significant technological achievement in ancient architecture, were objects of fascination and stories. The most popular of these featured the Devil, either as the builder of the bridge (relating to the precariousness or impossibility of such a bridge to last or exist in the first place) or as a pact-maker (sharing the necessary knowledge to build the bridge, usually in exchange for the communities souls). The legend attached to the bridge sketched by Lister is of the latter, and was related by Johann Jakob Scheuchzer in 1716. According to Scheuchzer, the people of Uri recruited the Devil for the difficult task of building the bridge. In return for his expertise, the Devil requested the soul of the first thing to pass the bridge. To trick the Devil, the people of Uri sent across a dog by throwing a piece of bread, and the dog was promptly torn to pieces by the Devil. Reference: Scheuchzer, J. , 1747 [1716]. Naturgeschichte des Schweitzerlandes. Vol. 2: 94. -

Einstein's abstracts
Cibachrome on aluminium. Microscopic magnification of Einstein’s equations from a blackboard that had been preserved in the History of Science Museum in Oxford -

The South African College
“UCT was founded in 1829 as the South African College, a high school for boys. The College had a small tertiary-education facility that grew substantially after 1880, when the discovery of gold and diamonds in the north – and the resulting demand for skills in mining – gave it the financial boost it needed to grow. The College developed into a fully fledged university during the period 1880 to 1900, thanks to increased funding from private sources and the government. During these years, the College built its first dedicated science laboratories, and started the departments of mineralogy and geology to meet the need for skilled personnel in the country's emerging diamond and gold-mining industries” (University of Cape Town 2021). -

Aurora Borealis
Extract from 'What to Observe', 1841, written by Julian Jackson (The Royal Geographical Society) -

SP-368 Biomedical Results of Apollo
Electrocardiograph signal received at Mission Control during various periods of the Apollo 11 mission -

Resonance
Demonstration of sympathetic vibration using the optical (flame) microphone


